Environment
-
From Scraps to Sips: Everyday Biomass Produces Drinking Water from Thin Air
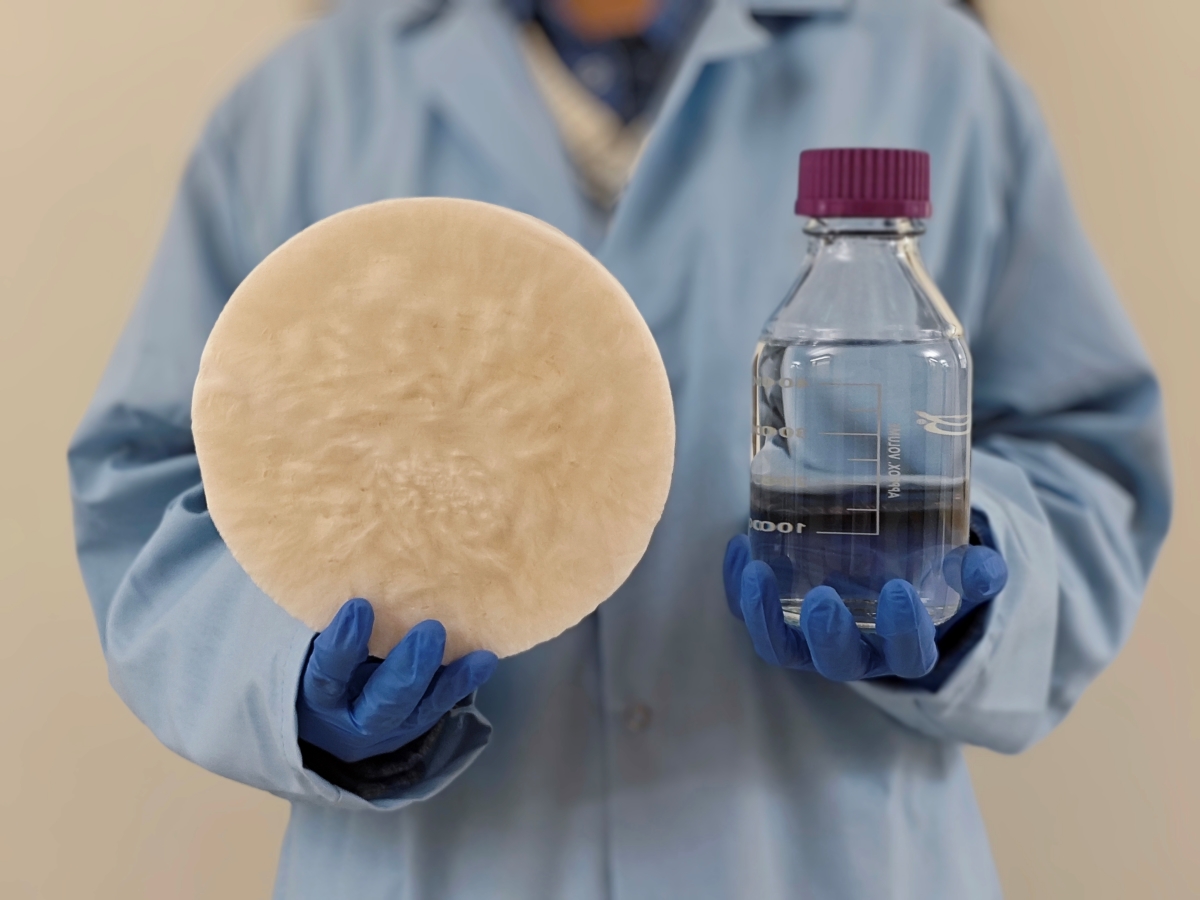

Discarded food scraps, stray branches, seashells and many other natural materials are key ingredients in a new system that can pull drinkable water out of thin air developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin.
-
Long-Term, Multi-Institutional Study on Health Impacts of Los Angeles Wildfires Launched
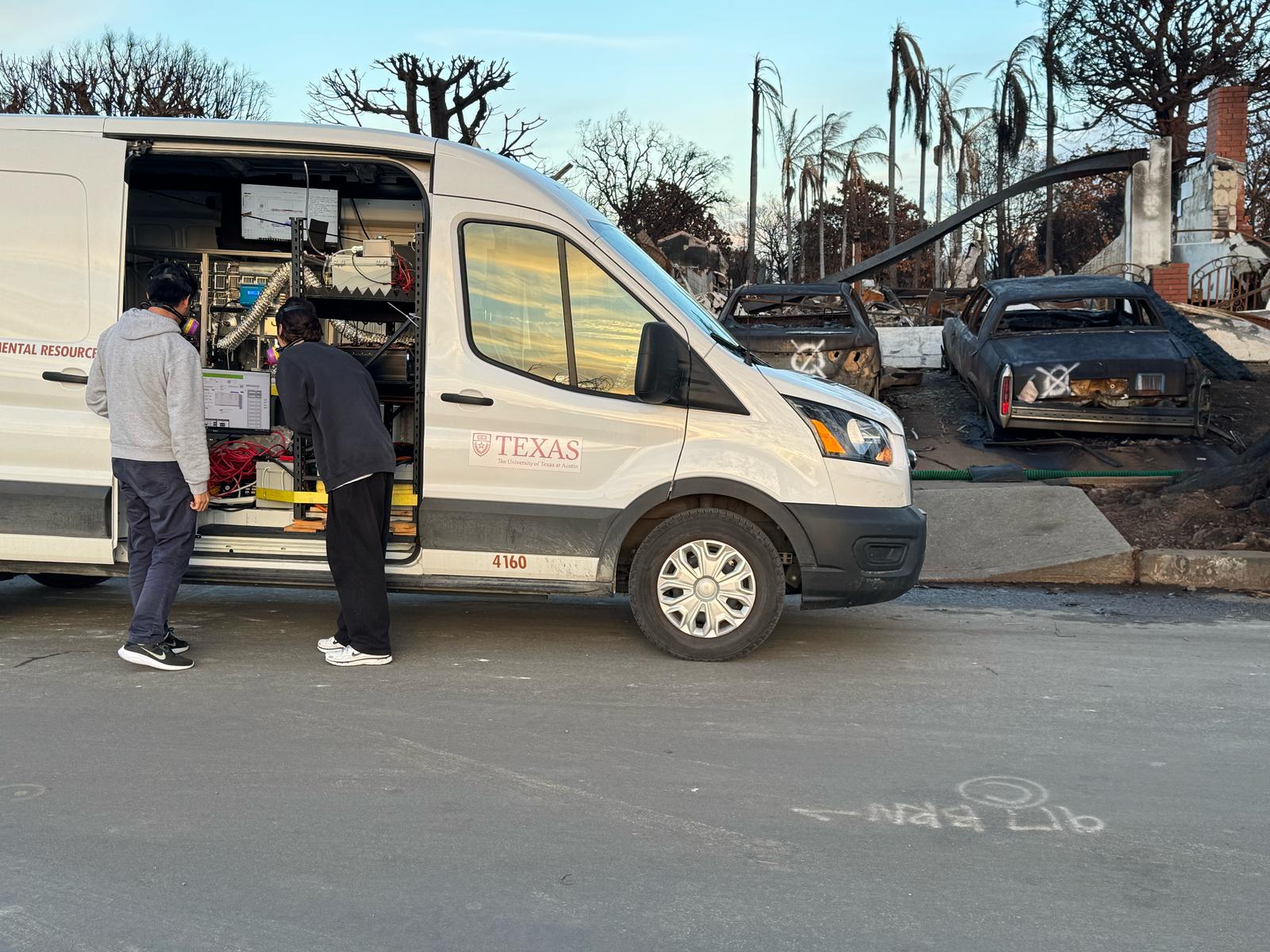

Texas Engineers are part of a team from four universities studying short- and long-term health impacts of the devastating wildfires in California.
-
Subtle Sinking of Gulf Coast Poses Substantial Flood Risks

Researchers mapped nearly 51,000 square miles of the Texas and Louisiana Gulf Coast using advanced satellite technology and found widespread land subsidence that was previously too difficult to detect.
-
Extreme Heat Impacts Daily Routines and Travel Patterns, Study Finds

A new study reveals that extreme heat significantly alters how people go about their daily lives, influencing everything from time spent at home to transportation choices.
-
Most Cities Receive More Rainfall Than Surrounding Rural Areas, Global Study Shows

In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers at The University of Texas at Austin found that more than 60% of cities in a survey of 1,056 regions around the world receive more precipitation than their surrounding rural areas.
-
Guihua Yu Wins Falling Walls Engineering and Technology Award
Texas Engineer Guihua Yu has been honored for his work to generate clean, drinkable water using solar energy.
-
How Plasmas Could Help Reduce Methane Emissions

Texas Engineers have developed the most efficient method yet to convert methane to methanol over the distributed scales where it is produced.
-
Smart Soil Can Water and Feed Itself

A newly engineered type of soil can capture water out of thin air to keep plants hydrated and manage controlled release of fertilizer for a constant supply of nutrients.
-
New Carbon Storage Technology Is Fastest of Its Kind

A new way to store carbon captured from the atmosphere developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin works much faster than current methods without the harmful chemical accelerants they require.
-
How Lasers and 2D Materials Could Solve the World's Plastic Problem
A global research team led by Texas Engineers has developed a way to blast the molecules in plastics and other materials with a laser to break them down into their smallest parts for future reuse.
-
Inspired by Nature
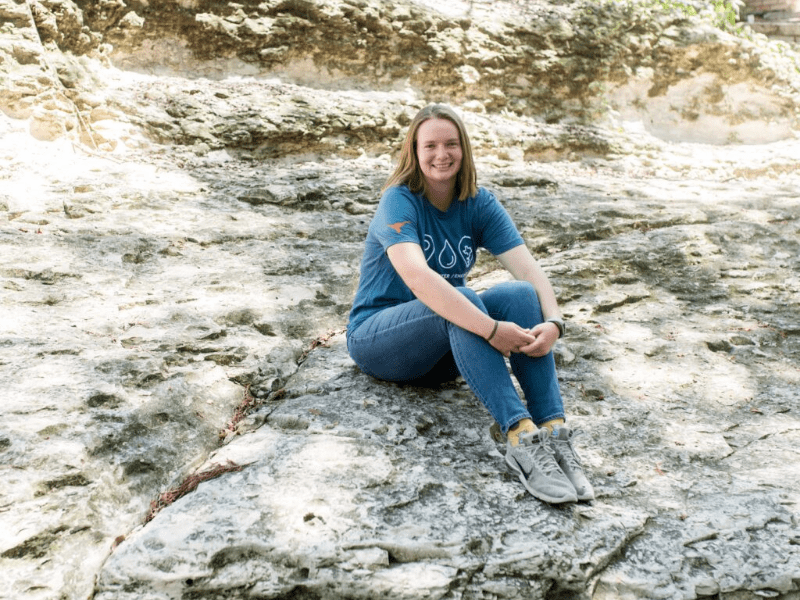

Civil engineering senior Savanna Smith has a particular interest in biomimicry.
-
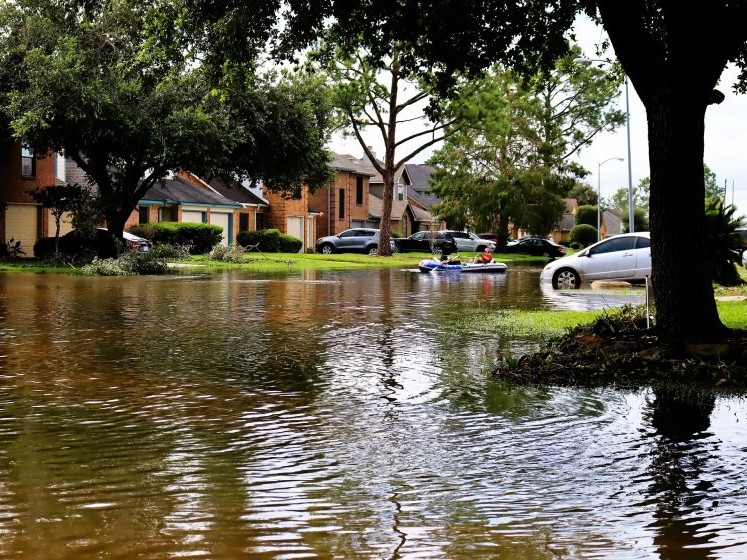
A Storm Surge of Optimism

One year after Hurricane Harvey shook the Lone Star State to its core, some coastal towns may never be the same again.
-
Texas Engineers in Alaska
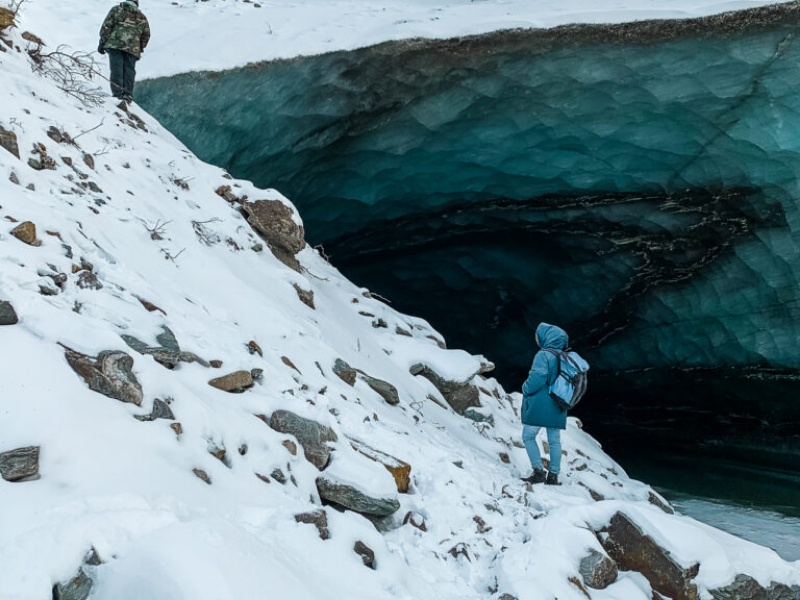

A new approach to protecting Native water supply
-
How Potatoes, Corn and Beans Led to Smart Windows Breakthrough

A study from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin aims to reduce the costs of smart windows by creating a new type of electrochromic device and materials.
-
Texas Engineers Use Erwin Center as Blueprint for Sustainable Demolition
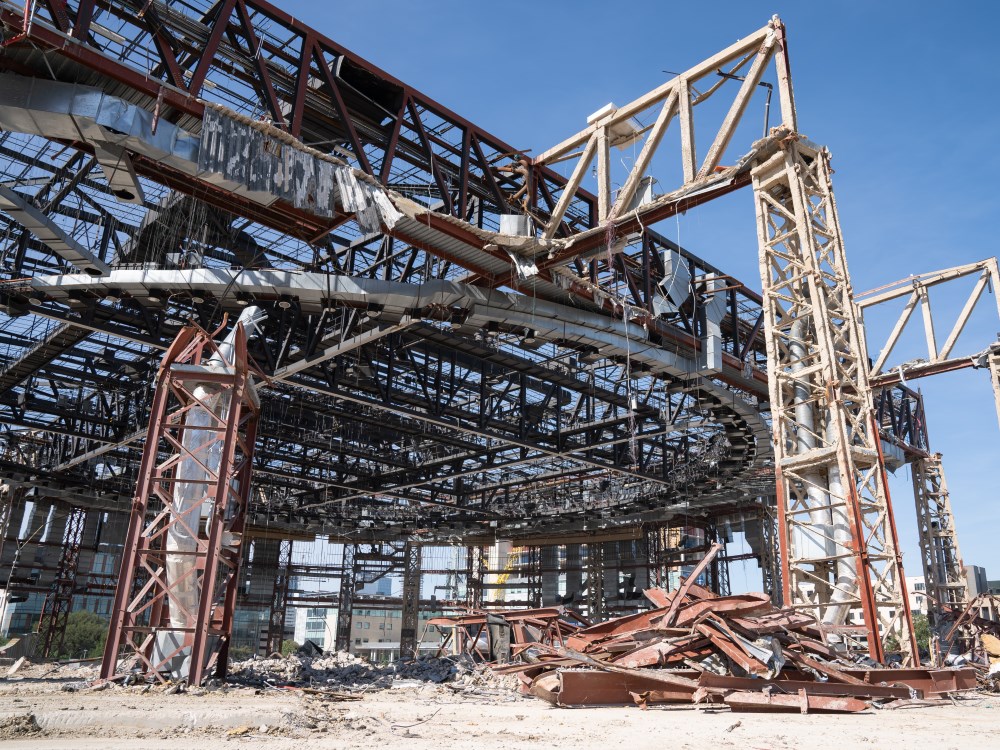

The Frank Erwin Center is coming down to make way for a new UT Austin-MD Anderson Cancer Center joint medical campus, but even in its demise, the former home of Longhorn basketball and many memorable moments in Austin's musical history is serving an important purpose.
-
How AI Can Bolster Power Grid's Resistance to Weather, Cyberattacks
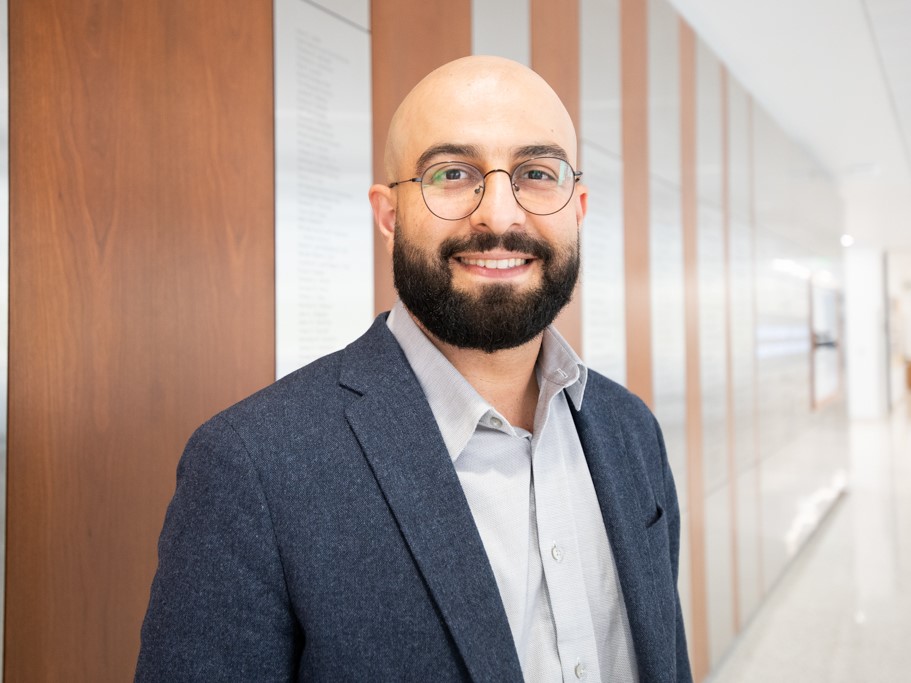

Texas Engineer Javad Mohammadi has dedicated his research to strengthening power grids, using artificial intelligence to make them more resistant to evolving threats.
-
Simulating How Big Waves Impact Shorelines
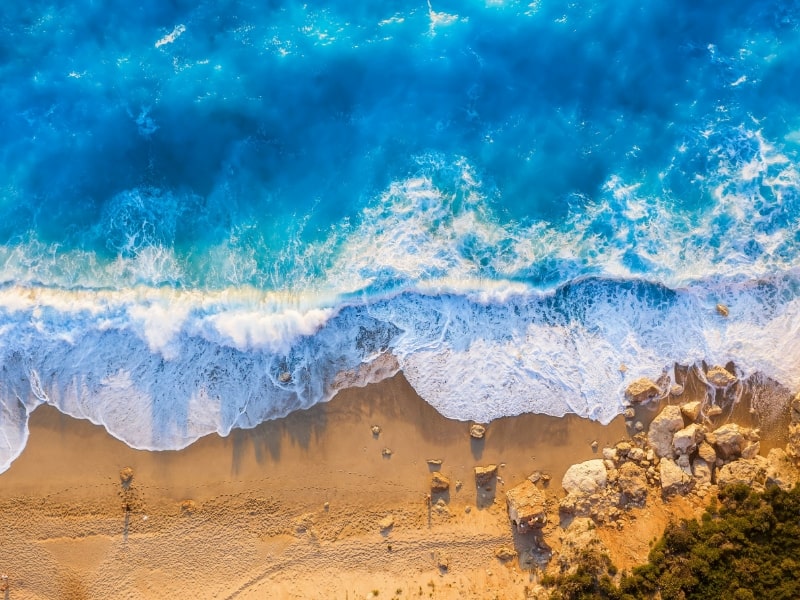

The crash of waves on the beach to many is the picture of peace and relaxation, but it’s also an important moment in the surrounding landscape. Known as the swash zone, where waves run up the face of the beach, this area is where crucial sand movement occurs, shaping the world’s coastlines over time and impacting flooding and other weather events.
-
Injectable Water Filtration System Could Improve Access to Clean Drinking Water Around the World
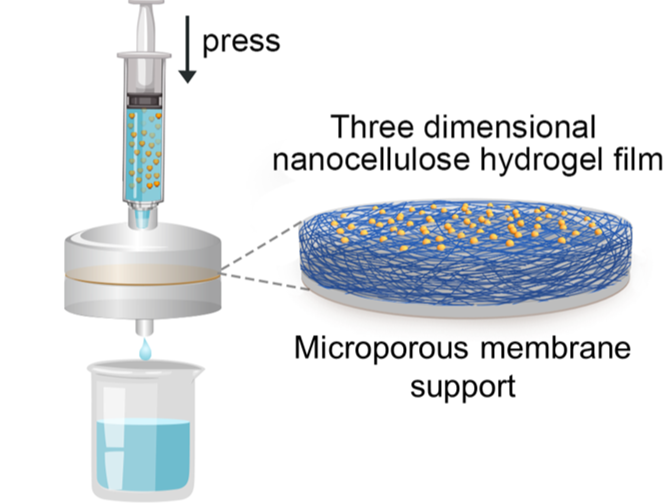
More than 2 billion people, approximately a quarter of the world’s population, lack access to clean drinking water. A new, portable and affordable water filtration solution created by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin aims to change that.
-
AI-Powered Civil Engineering: New NSF-backed Community Aims to Transform U.S. Infrastructure

Texas Engineers are creating a new community to unite civil engineers, cyberinfrastructure professionals and experts in artificial intelligence to better understand and protect our virtual and physical infrastructure.
-
Measuring Underwater Carbon Capture With Sound

Texas Engineers will lead a new project on marine carbon dioxide removal, capture and storage as part of a larger research push from the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE).







