Grants
-
Can AI Make Critical Communications Chips Easier to Design?
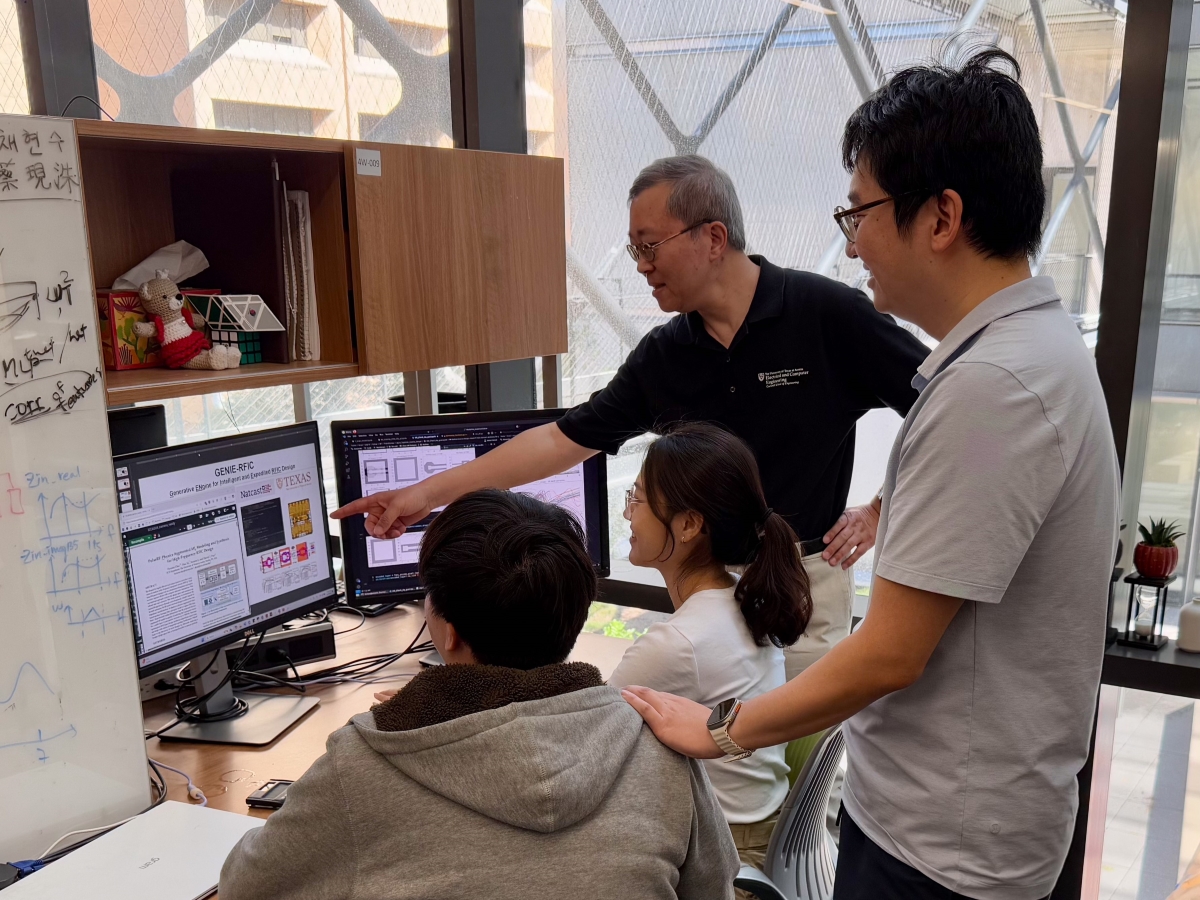

A multi-university team with heavy involvement from industry leaders plans to infuse artificial intelligence into the design process for radio frequency integrated circuits to reduce the difficulty of making these important chips.
-
UT Expertise to Reduce Emissions from Oil and Gas and Improve Measurement Accuracy

The University of Texas at Austin will play a leading role across multiple projects that collectively seek to drive down methane emissions across oil and natural gas value chains.
-
Texas Engineer Seeks to Decode Life's Building Blocks
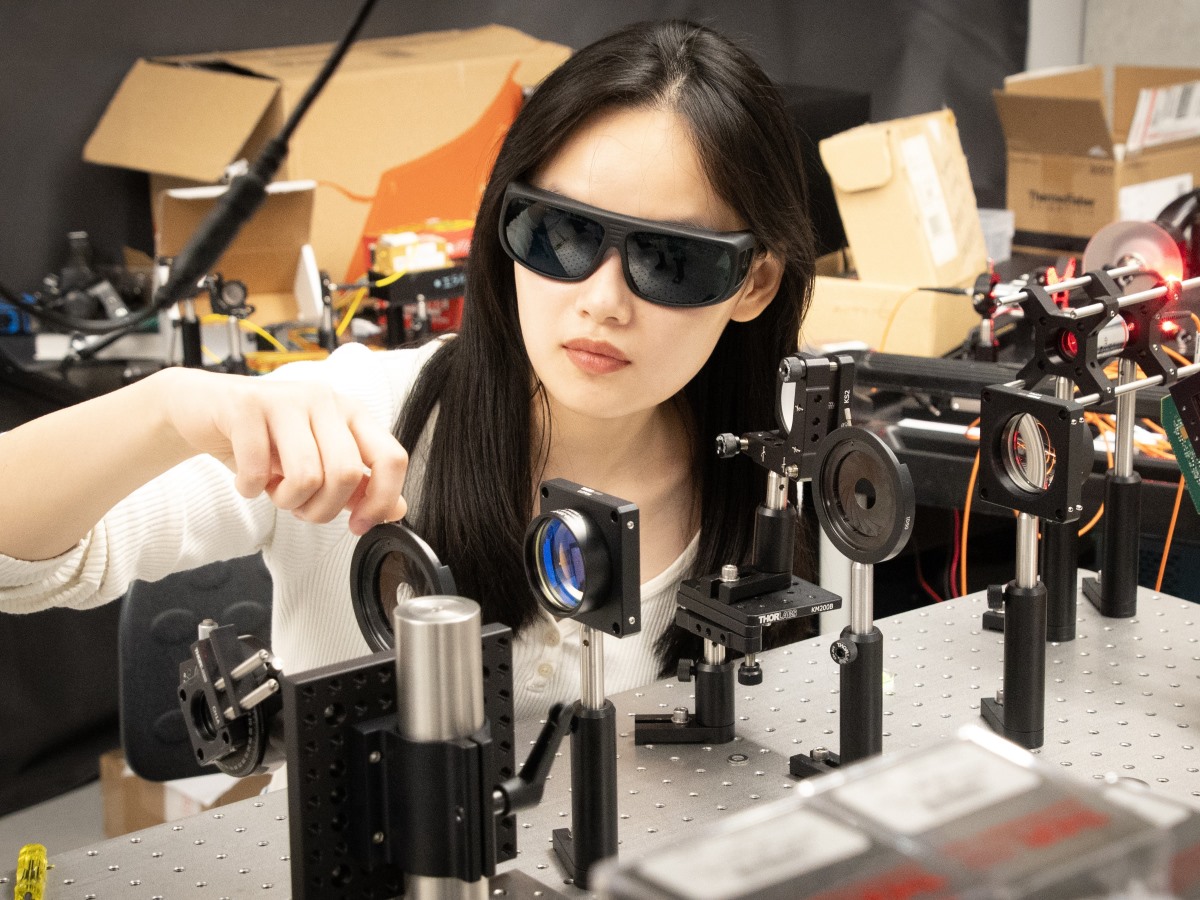
Shwetadwip Chowdhury, assistant professor in the Chandra Family Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering at The University of Texas at Austin, received a National Institutes of Health grant to study how complex organisms develop.
-
Texas Engineers Part of Huge NSF Semiconductor Program
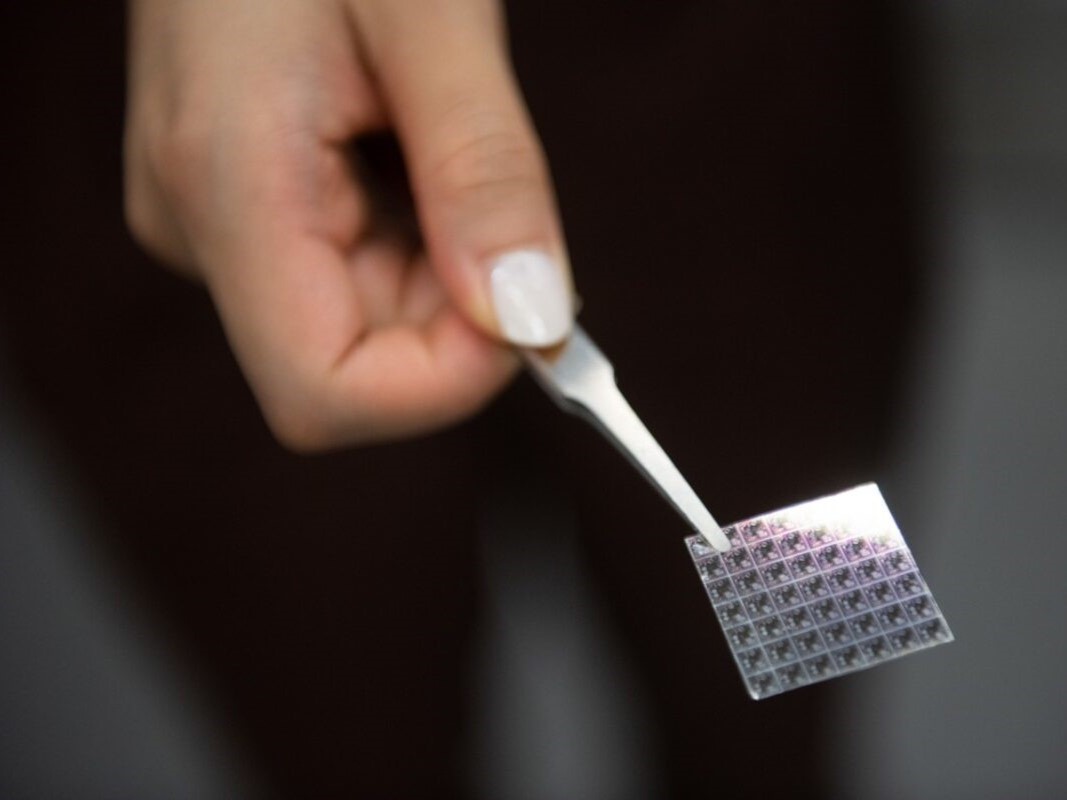
Texas Engineers will develop next-generation semiconductor technologies as part of a collaboration of the National Science Foundation and leading industry companies.
-
Could Hydrogen, Ammonia Blends Become the Key to Clean Electricity?
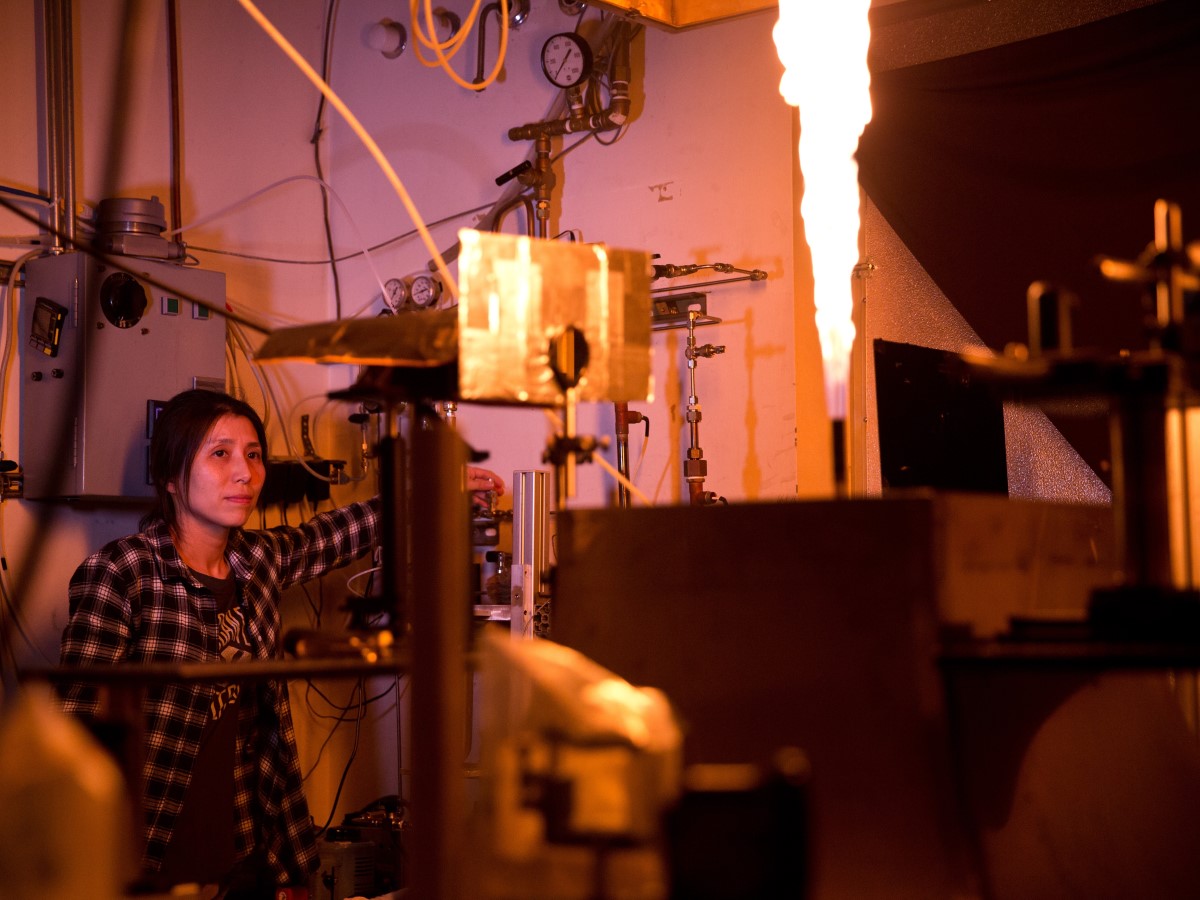
Texas Engineers are combining hydrogen and ammonia, which are in many ways natural complements, as a potential source for generating carbon-free electricity
-
Next-Level Breast Reconstruction After Cancer

Texas Engineers are part of a multi-institutional research team designing custom molds for breast cancer patients who undergo reconstructive surgery.
-
UT Awarded $840M To Build Microelectronics Manufacturing Center, Advance U.S. Semiconductor Industry
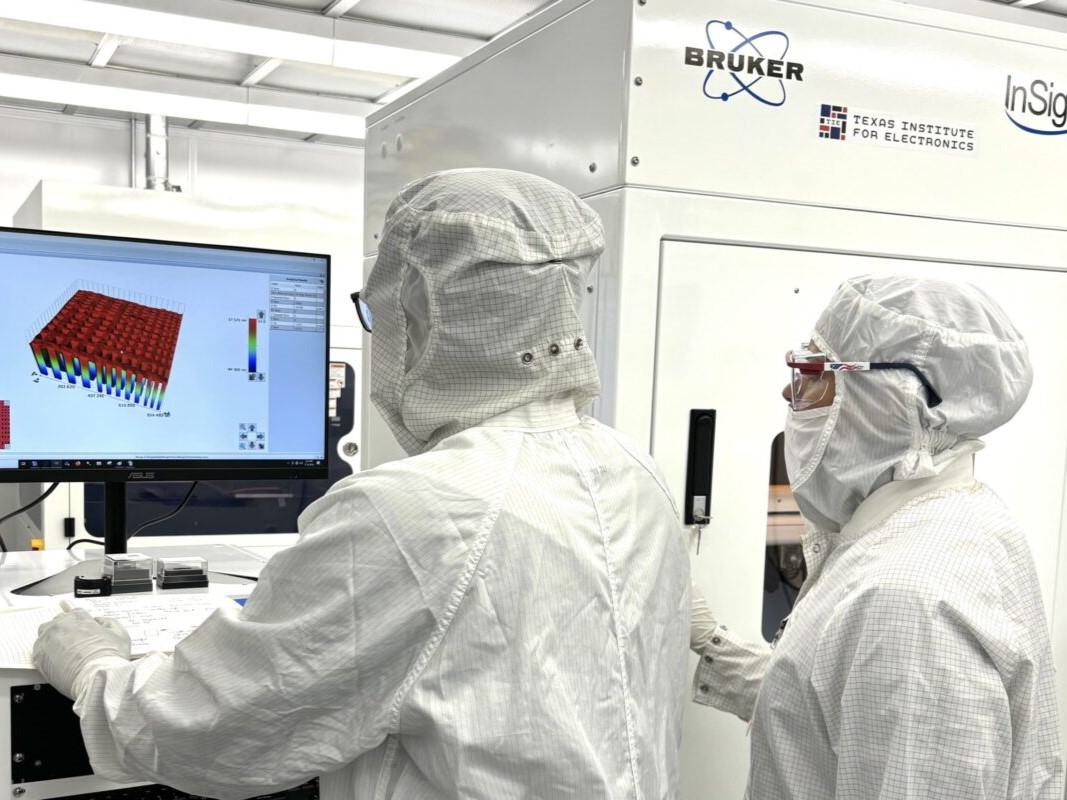

The Texas Institute for Electronics (TIE) at The University of Texas at Austin has been selected to engineer the next generation of high-performing semiconductor microsystems.
-
Texas Engineers Join Space Force Operation, Bringing Robots to Space

Texas Engineers are participating in a groundbreaking U.S. Space Force operation that will propel innovative technologies for in-space operations.
-
Self-Propelling Satellites and Reentry Shields Among New Projects for Aerospace Engineer
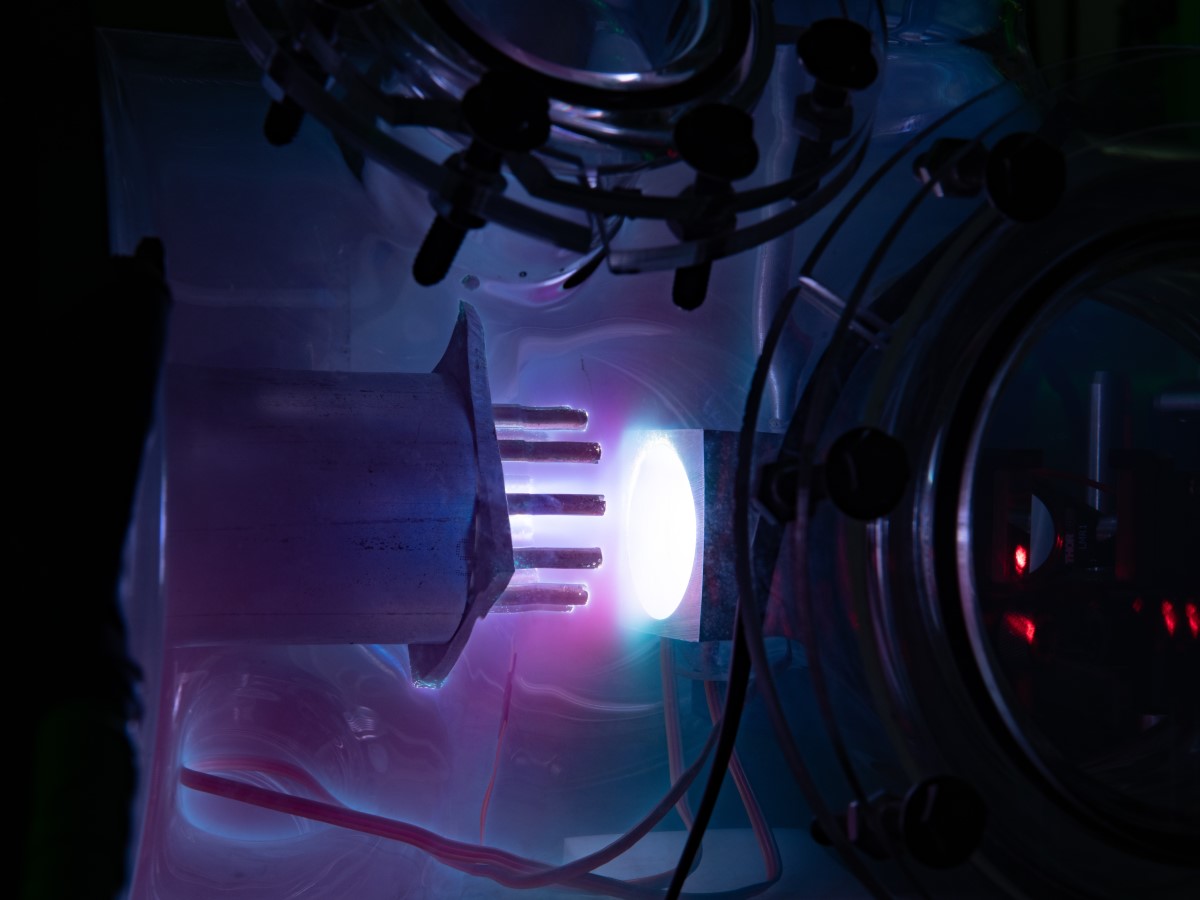

Aerospace engineer Thomas Underwood is studying many applications of plasmas, which involve the infusion of electrical energy into gases.
-
Measuring Light and Matter with More Precision
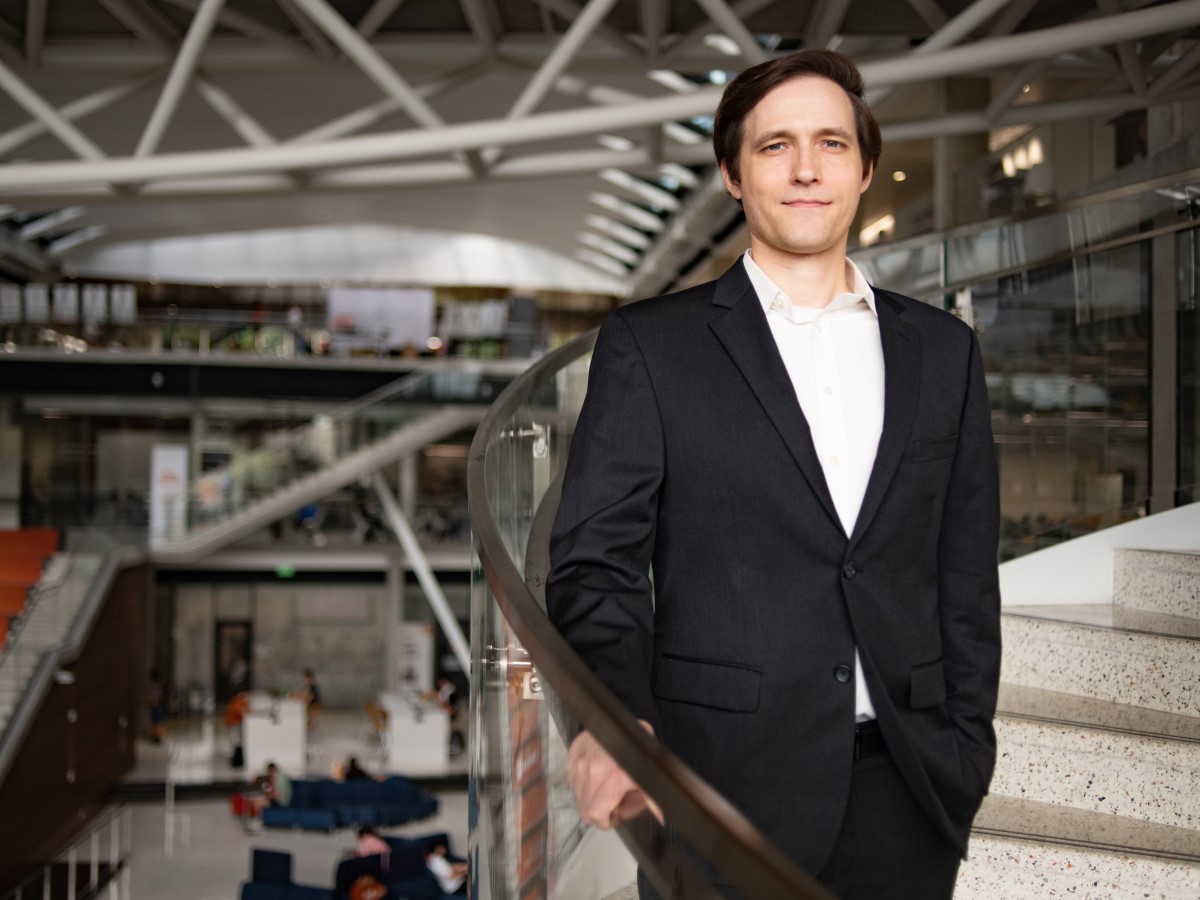

David Burghoff plans to optimize measurements in astronomy, remote sensing and quantum information processing through a new Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative (MURI).
-
Novel MRI Approach Aims to Spot Kidney Disease in All Populations
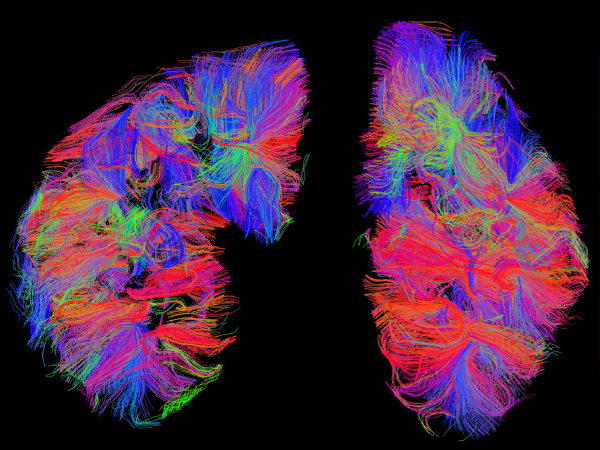
A new grant from the National Institutes of Health will support a pair of Texas Engineers in their development of novel MRI scans for detecting kidney disease.
-
Simulating How Big Waves Impact Shorelines
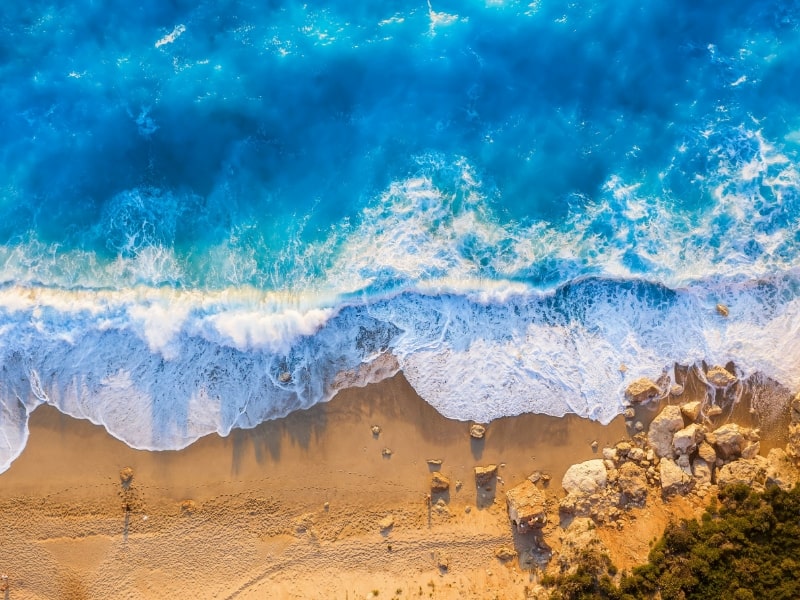

The crash of waves on the beach to many is the picture of peace and relaxation, but it’s also an important moment in the surrounding landscape. Known as the swash zone, where waves run up the face of the beach, this area is where crucial sand movement occurs, shaping the world’s coastlines over time and impacting flooding and other weather events.
-
Cockrell Battery Experts Team with John Deere to Electrify Farm and Construction Vehicles

Texas Engineers are working with John Deere to develop technologies to electrify agriculture vehicles like tractors.
-
Texas Engineers Receive Funds Through Joint French Science Program

A pair of Texas Engineers are teaming up with scientists from France as part of a six-year-old collaborative research program.
Delia Milliron and D. Nicolas Espinoza were among the 2023 awardees of the Dr. Cécile DeWitt-Morette France-UT Endowed Excellence Fund.
-
AI-Powered Civil Engineering: New NSF-backed Community Aims to Transform U.S. Infrastructure

Texas Engineers are creating a new community to unite civil engineers, cyberinfrastructure professionals and experts in artificial intelligence to better understand and protect our virtual and physical infrastructure.
-
New Grant Aims to Gain Control Over Disordered Materials

A new class of designer gels is on the way, potentially packed with a combination of properties that have traditionally been mutually exclusive to either stiff or soft materials.
-
Texas Engineers Land Semiconductor Grants Through CHIPS Act-Backed NSF Program

A pair of Cockrell School research teams are part of a massive semiconductor grant program from the National Science Foundation that includes funds from industry leaders and the federal CHIPS Act.
-
Texas Engineers Lead Cislunar Space Research Coalition

The University of Texas at Austin will spearhead a groundbreaking research collaboration to advance the U.S. Air Force’s ability to understand and monitor activity in cislunar space. The project itself, officially named the “Representations, Theory, and Algorithms for Autonomous Space Domain Awareness in the Cislunar Regime,” seeks to tackle the intricate complications of monitoring and controlling activities within the expansive region between Earth and the moon.
-
The Future of Materials Is One Step Closer

A technological leap sits on the horizon, with exciting capabilities like quantum computing, soft robotics and more coming down the pike. To bring these ideas to reality will require engineering new classes of materials that make up their building blocks.
The Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials at The University of Texas at Austin has been on the leading edge of materials development for the past six years. With a fresh infusion of funding from the National Science Foundation (NSF), the center will turn its attention to new research thrusts that will bring to life materials with enhanced properties and capabilities.
-
New Research Aims to Fix Machine Learning’s Struggle with Uncertainty

When new technology meets the real world, dynamic challenges threaten to derail progress, like a self-driving car that struggles to perceive rapid changes in the environment and adjust.







