Grants
-
Eliminating CO2 Emissions from Manufacturing the Goal of Major Research Alliance

An alliance of nine universities, three national labs and 37 companies will tackle one of the biggest hurdles to decarbonizing manufacturing: carbon dioxide emissions from generating process heat.
Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin will play a significant role in the effort that aims to replace the energy source that powers most manufacturing processes, swapping out hydrocarbon fuels for clean electricity – generated through renewable sources such as solar and wind. Doing this could make a major impact, as manufacturing represents more than 30% of U.S. carbon dioxide emissions.
-
Chest E-Tattoo Boasts Major Improvements in Heart Monitoring
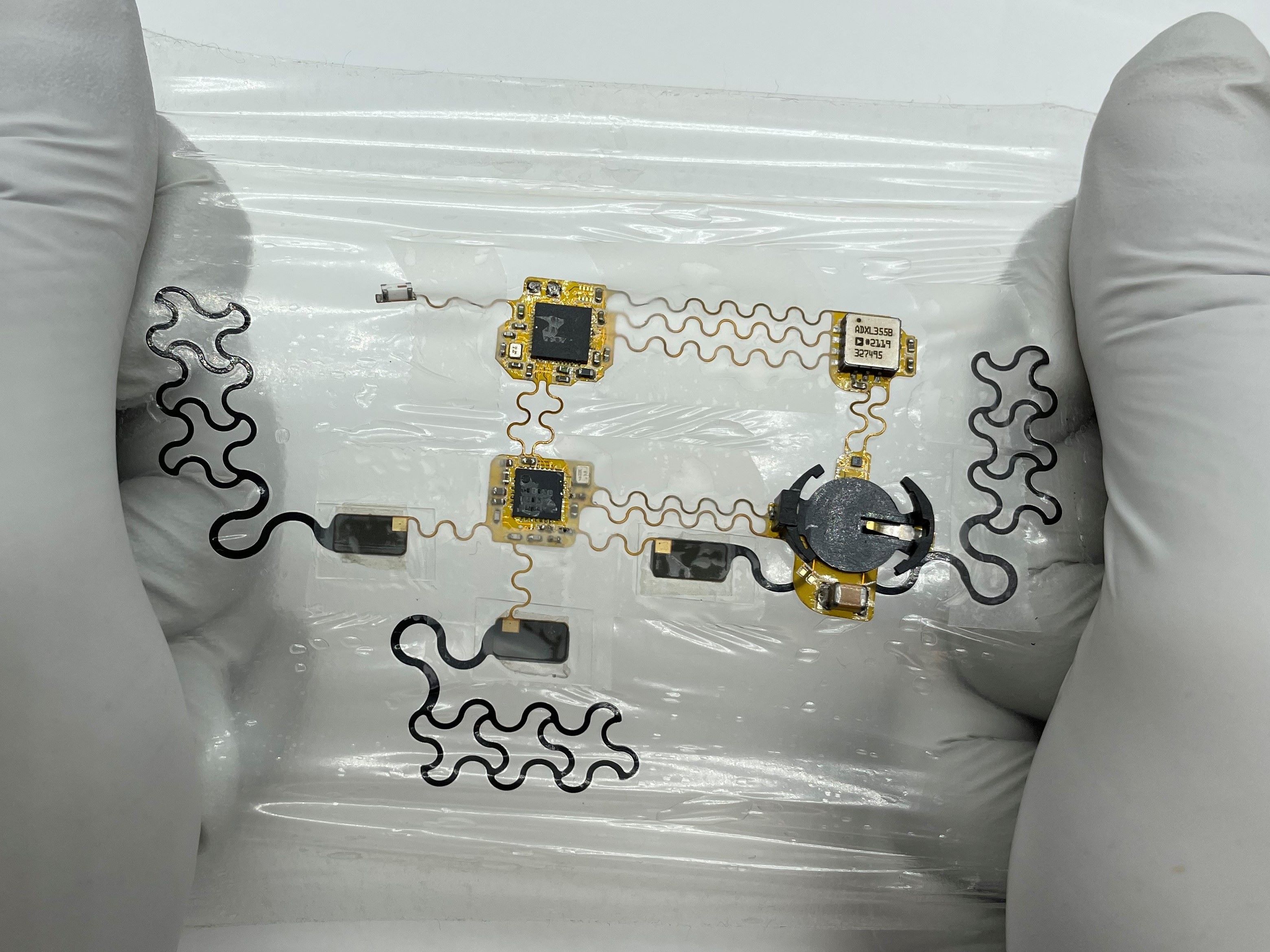
A new flexible, wearable medical device could provide a major boost in the fight against heart disease, the leading cause of death in the United States.
A team led by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin has developed an ultrathin, lightweight electronic tattoo, or e-tattoo, that attaches to the chest for continuous, mobile heart monitoring outside of a clinical setting. It includes two sensors that together provide a clear picture of heart health, giving clinicians a better chance to catch red flags for heart disease early.
-
Researchers Eye New Ways to Prevent Agricultural Pests from Entering U.S.

Anyone who's traveled internationally is familiar with this standard question upon returning: "Did you bring back any fruits or vegetables?" This has to do with a larger effort from the U.S. government to prevent agricultural pests from entering the country within cargo shipments or passenger baggage, potentially threatening the nation's crops.
-
Dynamic Events in Thick Tissue are Nearly Impossible to Image; Texas Engineers Aim to Change That
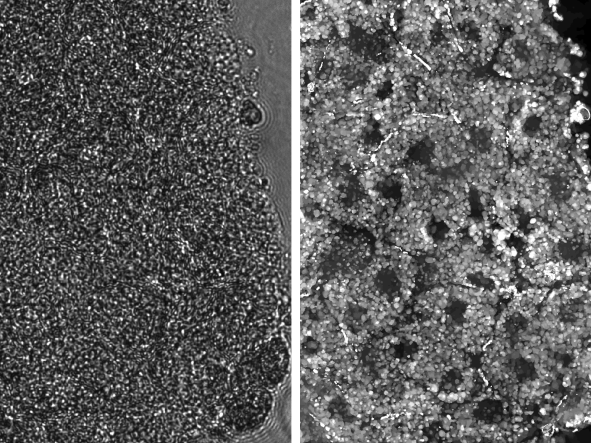
Today's state-of-the-art optical imaging technologies can help us see biological dynamics occurring at subcellular resolutions. However, this capability is primarily limited to thin biological samples, such as individual cells or thin tissue-sections and falls apart when it comes to capturing high-resolution, three-dimensional images of thicker and more complex biological tissue. This limitation occurs because tissue is composed of heterogeneous arrangements of densely-packed cells, which scatter light and hinder optical imaging. This is especially a challenge in live tissue, where biological dynamics occurring within the tissue further diffuse light and scuttle images.
-
New Transportation Research Center to Focus on Travel Behavior and Demand

The University of Texas at Austin is leading a new multi-university transportation research hub that will focus on evolving travel behaviors in the wake of technological advances and ongoing shifts in work habits.
The Center for Understanding Future Travel Behavior and Demand at UT Austin will execute what it calls the “Transportation Heartbeat of America Survey” to collect longitudinal data from people, institutions and businesses about changes in travel patterns. The goal is to emphasize a more people-centric approach to mobility analysis to ensure safe, reliable, equitable and sustainable travel on surface transportation systems.
-
Researchers Aim to 3D Print Kids Breathing Masks and Other Complex Medical Devices

Customized medical devices represent an intriguing application of additive manufacturing technology, also known as 3D printing. However, the capabilities to design and print the smart, flexible materials this type of equipment requires remains lacking.
Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and Penn State University just got a grant to change that. The $2 million grant from the National Science Foundation's LEAP-HI program will pave the way for the researchers to tackle the challenge of designing and 3D printing smart devices using multiple materials.
-
Surgical Standard for Skin Cancer Removal, Re-Imagined

The gold standard for removing benign skin cancers has been around since the 1930s. Although very accurate, it requires a full laboratory next door to the procedure room to determine whether the full tumor has been removed or not. A research group at The University of Texas at Austin is aiming to make that process more efficient and potentially expand access to this type of surgery to a broader population.
-
New Nanoscale 3D Printing Technique Could Solve Vexing Bottlenecks in High-Throughput Nanomanufacturing
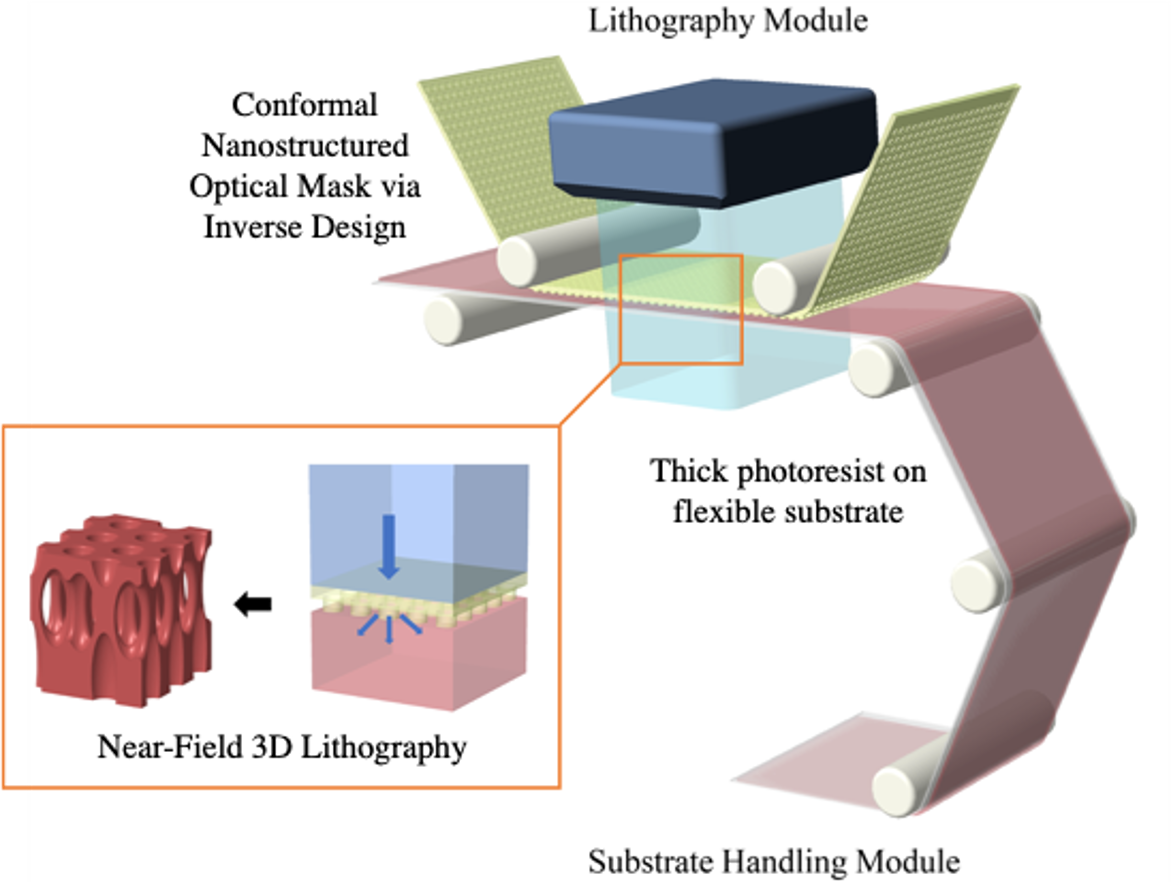
The University of Texas at Austin has a rich history in 3D printing, inventing one of the first forms of the technology, and now Texas Engineers have received a grant to tackle some of its most glaring problems.
In 3D printing, there is a tradeoff between the precision needed to create the object (resolution) and the speed and scale at which the object can be made (throughput). This is especially true at the nanoscale, where it is practically infeasible to make any kind of complex structure with multiple types of materials or patterns at a high rate.
-
Can Robots and Humans Co-exist in Public? UT Campus Study Will Offer Answers

Autonomous robots will soon rove the buildings and streets of The University of Texas at Austin campus. But unlike other commercial delivery services, this fleet of robots will help researchers understand and improve the experience of pedestrians who encounter them.
-
Texas Biologics to Bolster Research in Therapeutics

Nearly two years after COVID-19 vaccines entered widespread use, featuring technology from researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, the Cockrell School of Engineering and the College of Natural Sciences have launched Texas Biologics, a cross-disciplinary effort made up of world-renowned faculty members and researchers working across all areas of therapeutics.
-
Space Environmentalist Awarded ‘Genius Grant’ by MacArthur Foundation
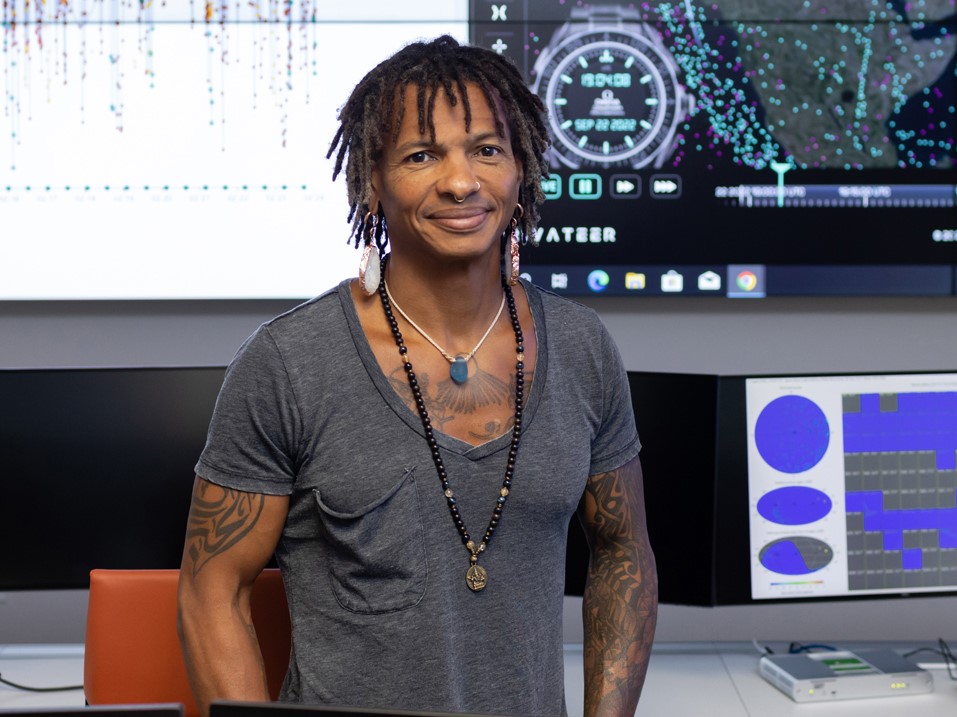

Moriba Jah, an astrodynamicist, space environmentalist and aerospace engineer at The University of Texas at Austin, has been awarded a MacArthur Fellowship, often referred to as the “genius grant.” The award recognizes Jah’s work to track and monitor the more than 30,000 human-made objects orbiting the earth.
-
Texas Universities Partner to Study Combined Impact of Flooding and Air Pollution in Beaumont-Port Arthur
Four Texas universities, led by The University of Texas at Austin, have been awarded a grant to establish a new research center to study the risks and impacts of flooding and air pollution in a fast-growing part of Southeast Texas. The scientists will focus on the interactions between these two key issues, as well as their potential acceleration under various climate scenarios.
-
Interdisciplinary Team Aims to Create Controllable Synthetic Cells and Tissue
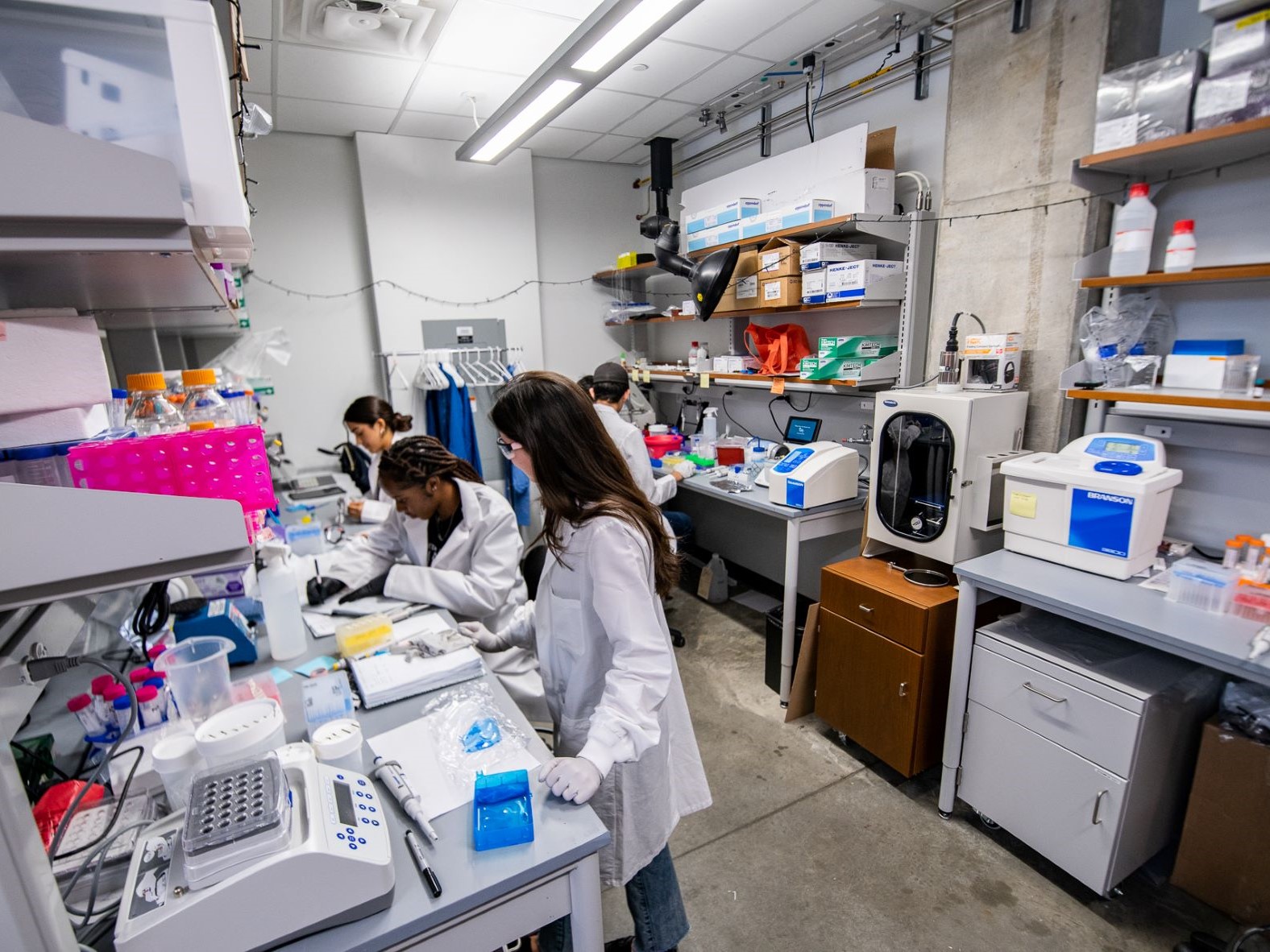

A new grant for researchers across several departments and schools at The University of Texas at Austin aims to establish a new hub of activity to better understand and replicate the skills that cells possess. The grant from the National Science Foundation will support a platform for creating synthetic cells with an emphasis on how they link up and exchange material and information with one another.
-
Manuel Rausch Wins NIH R01 to Make Way for Early Intervention of Tricuspid Valve Leakage
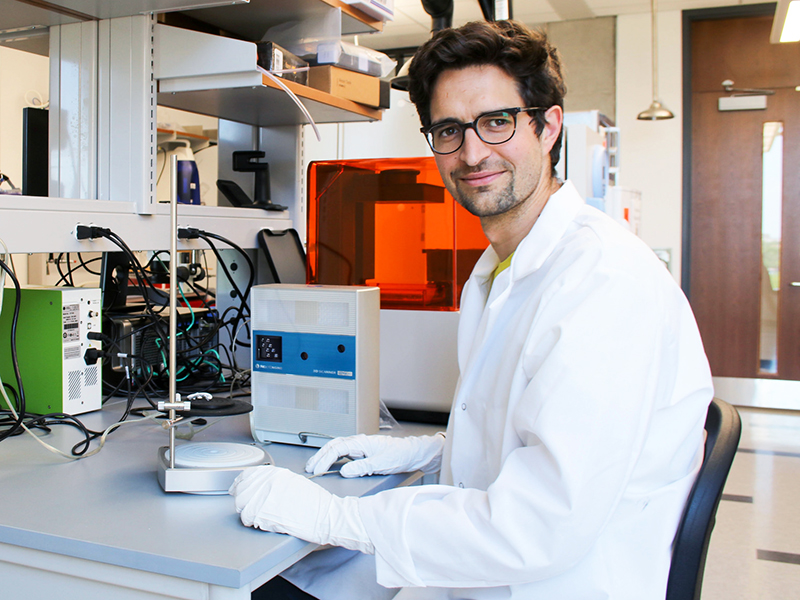

Manuel Rausch, an assistant professor with appointments in the Department of Aerospace Engineering and Engineering Mechanics and the Department of Biomedical Engineering, has received a prestigious R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health in the amount of $3.9 million. He will use the funding to lead a study of the heart’s tricuspid valve to better understand functional tricuspid valve regurgitation (FTR) – a condition that causes leakage of the valve located between the right atrium and the right ventricle of the heart.
-
Transportation Research Center Gets Phase 2 NSF Grant

A group of four universities, including The University of Texas at Austin, recently won a grant from the National Science Foundation for the second phase of their Industry-University Cooperative Research Center. The Center for Efficient Vehicles and Sustainable Transportation Systems (EVSTS) works closely with automobile makers to tackle pressing challenges of making vehicles more sustainable, connected and efficient.
-
Researchers to Develop Digital Twin Platform for Enhanced Storm Mitigation

More than half of the U.S. population lives in coastal watershed counties or parishes. Coastal communities along the Gulf of Mexico are among the most heavily populated – also a region where high concentrations of energy resources have made it a national hub for many large-scale carbon-to-capture storage facilities.
-
New Grant for Photovoltaics Research Center Will Support Net Zero Push
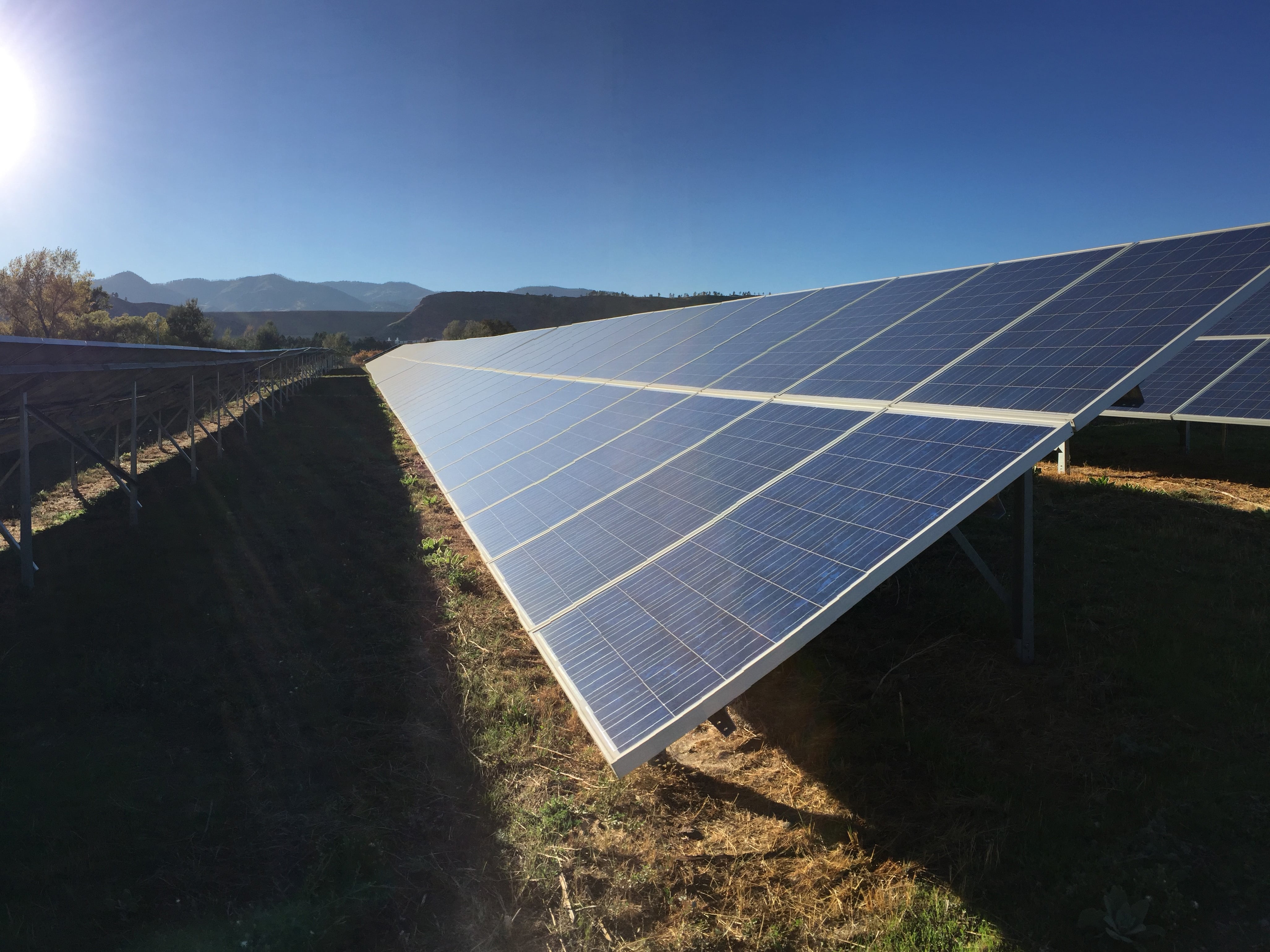

Solar has undergone a transformation over the past 10 years. In 2011 in the U.S., photovoltaic devices, or solar cells, provided enough electricity to power about 170,000 homes. As of May 2021, solar accounted for 5.1% of the U.S. electricity mix — enough to power more than 12 million homes. This dramatic increase in the use of solar power is mostly due to technology advancements and reduced costs. Now, with major governmental and corporate entities setting net-zero carbon emissions goals by 2050, the use of solar-generated electricity must continue to grow even more in order to realize these sustainability targets. To contribute to these enormous goals, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has awarded a Phase III Industry/University Cooperative Research Center (IUCRC) grant to The University of Texas at Austin to lead the Center for Solar Powered Future (SPF2050) with partner institution Colorado State University.
-
UT Austin, Texas State University Land NSF Grant for New Materials Center

The University of Texas at Austin’s Center for Dynamics and Control of Materials (CDCM), a National Science Foundation Materials Research Science and Engineering Center (MRSEC), is partnering with Texas State University to establish the Center for Intelligent Materials Assembly. The new center is being developed through an NSF Partnerships for Research and Education in Materials (PREM) grant.
-
Texas Engineers Awarded DOE Grant to Study Engineered Geothermal Systems

Figuring out how to efficiently extract heat from the earth’s sub-surface and use it as a power source is a priority across the energy industry. Cockrell School engineers are on the front lines of this push to learn more about geothermal energy and the best ways to harvest and utilize it.
-
Unmanned Aerial Vehicles to Scale New Heights Thanks to NASA

NASA is funding a major project on the future of autonomous air cargo transportation, and The University of Texas at Austin will be playing a lead role. The COVID-19 vaccine rollout — the largest global logistics effort since World War II — has underscored the importance of increasing efficiencies in the global supply chain infrastructure. Autonomous aerial vehicles have the potential to revolutionize cargo transportation.








