Research Advancements
-
AI-Created Materials Could Make Your Energy Bill Cheaper
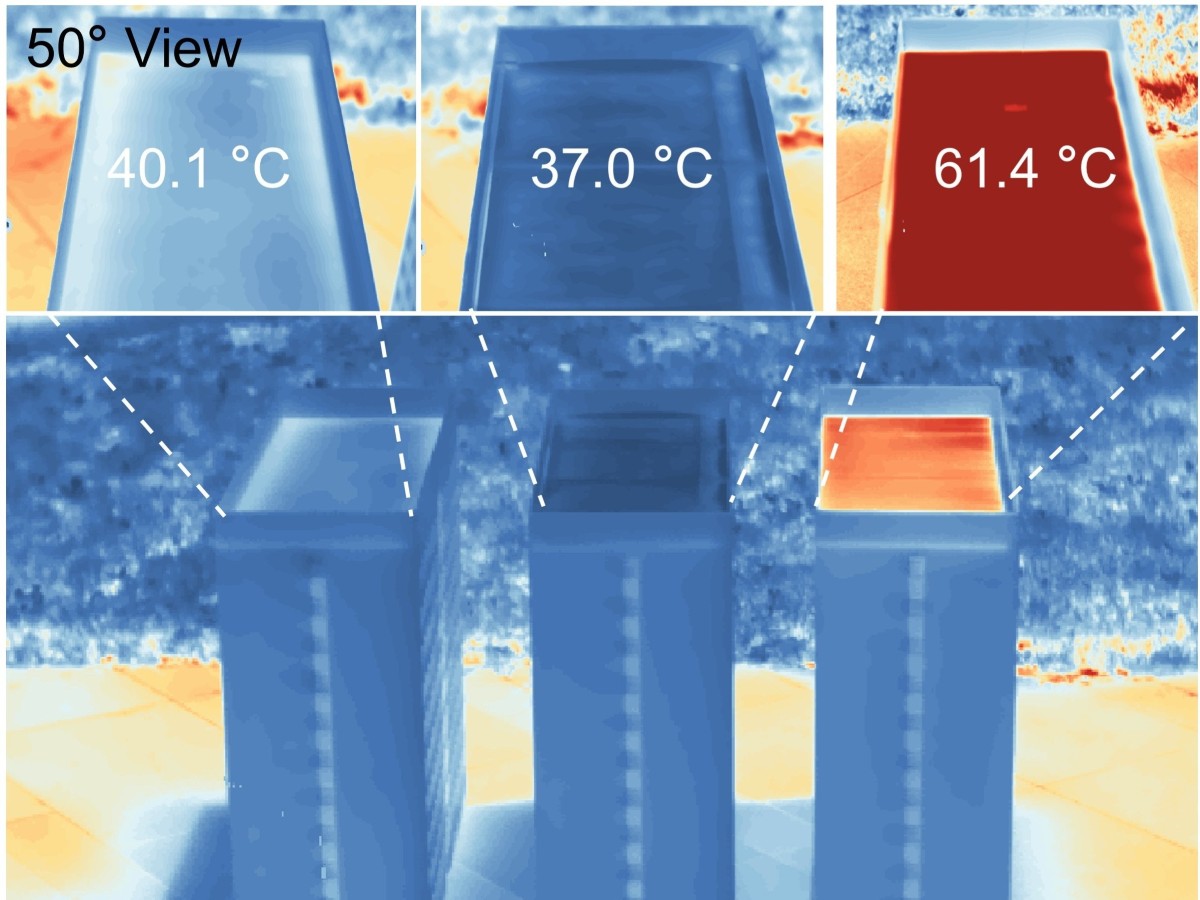
Texas Engineers developed new materials developed using machine learning and artificial intelligence to keep your house cooler and reduce energy bills.
-
AI Can Diagnose Your Heart in Just a Few Minutes
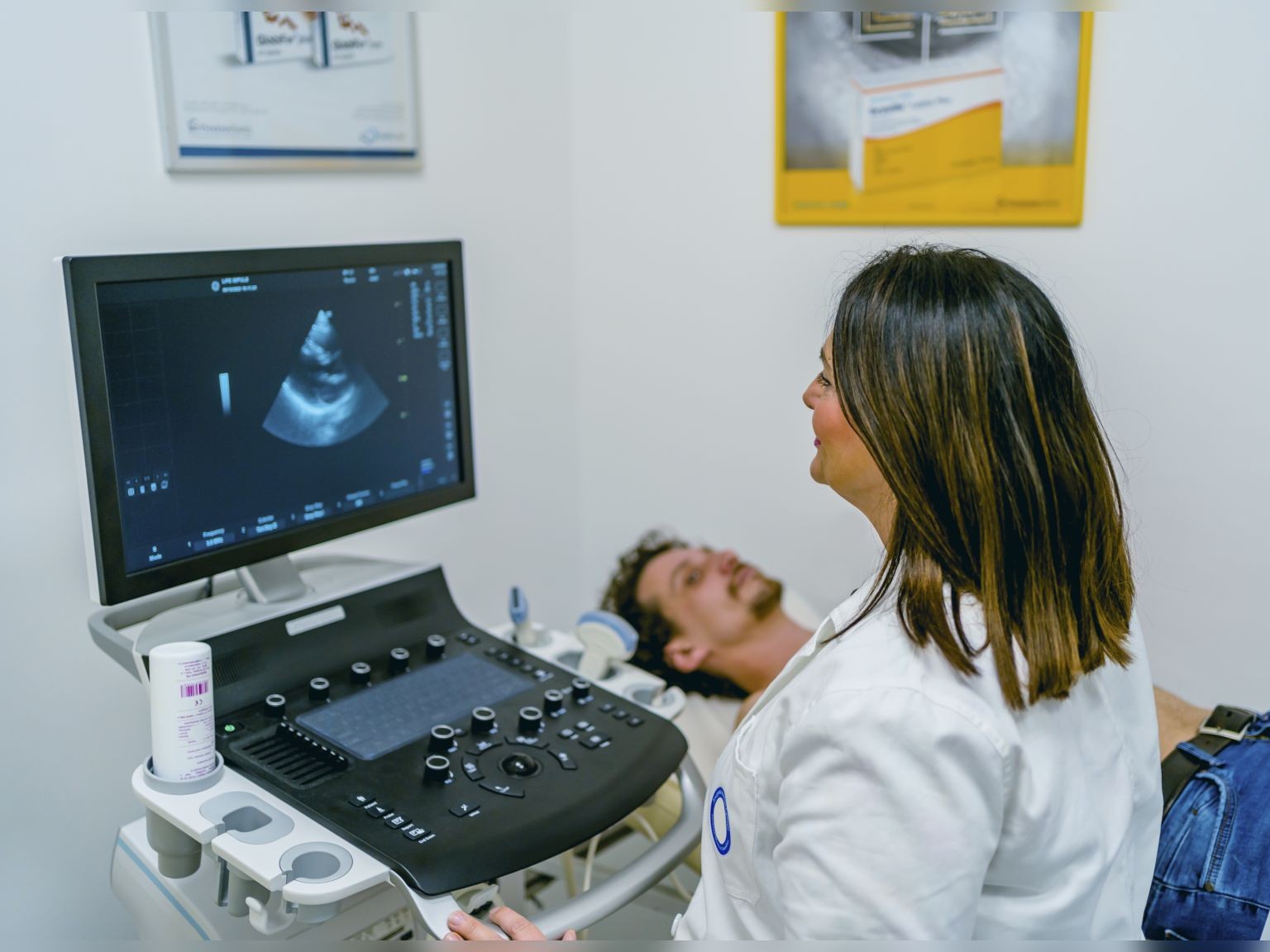
Texas Engineers worked with researchers from Yale School of Medicine to develop an artificial intelligence-enabled tool that can quickly and accurately interpret echocardiograms.
-
Restoring Damaged Paintings With AI 'Masks'
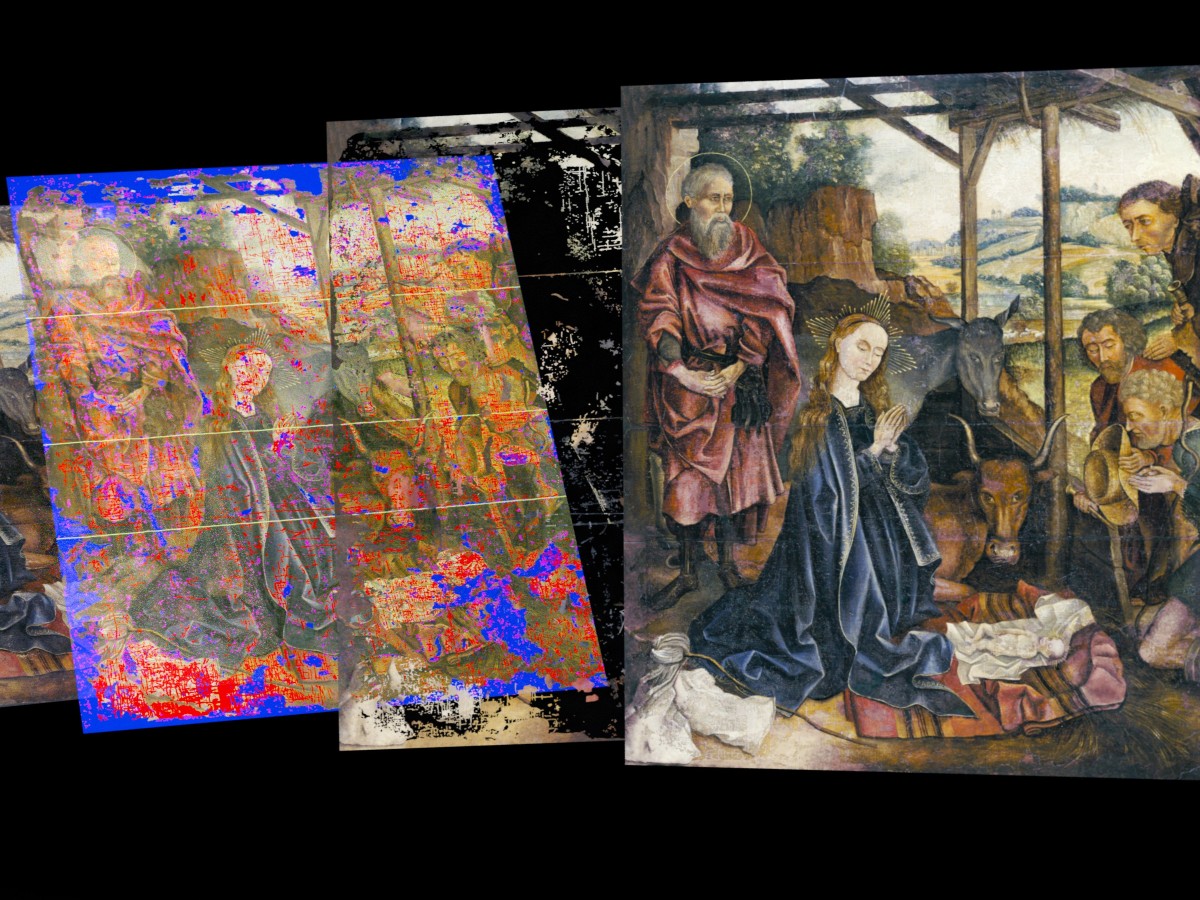

Texas Engineering alumnus Alex Kachkine developed a new method to physically apply a digital restoration directly onto a damaged painting.
-
A Jolt of Innovation for Brain-Computer Interfaces
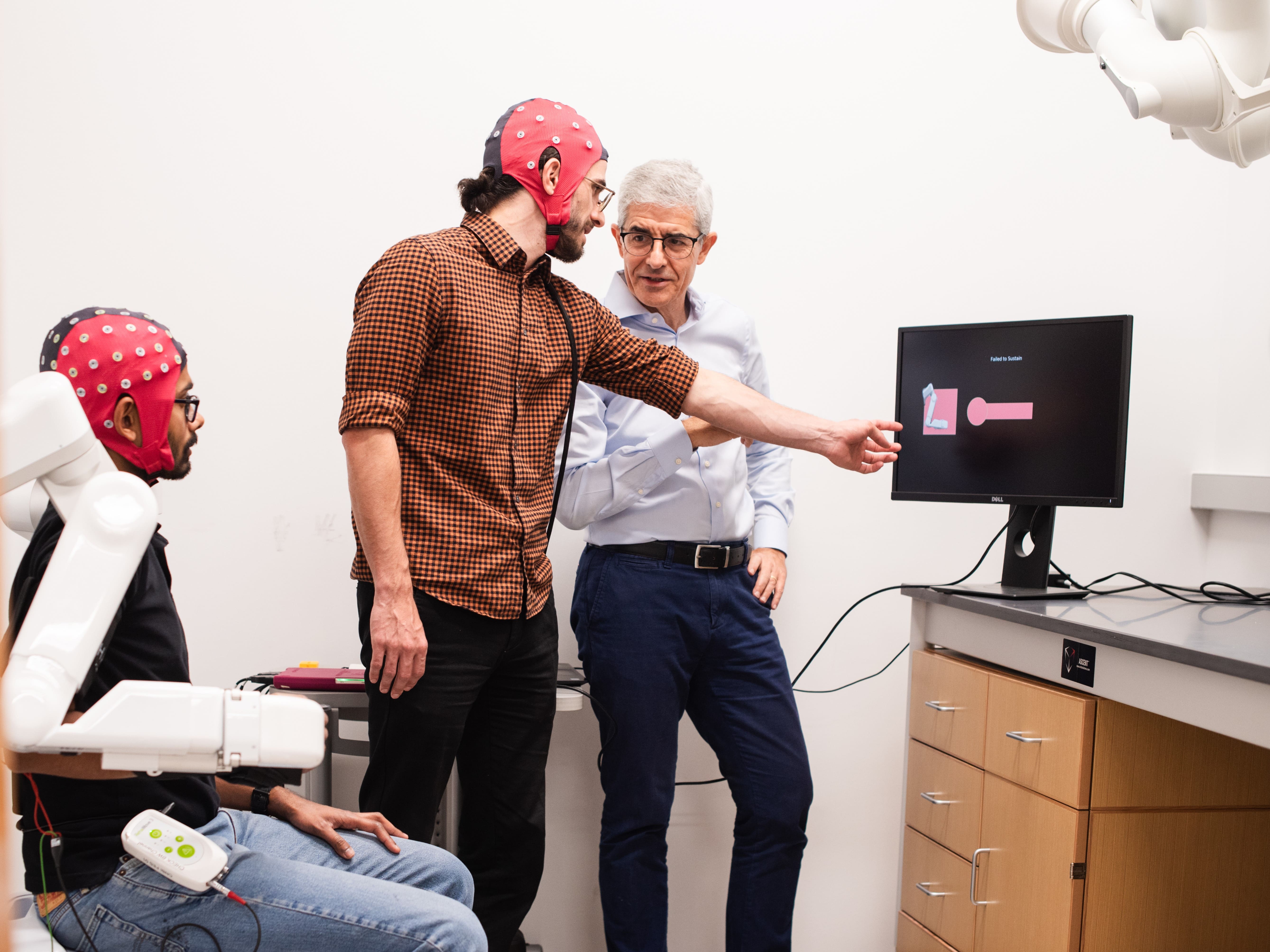

Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin discovered a novel way to accelerate the learning curve of brain-computer interfaces. These devices allow users to control things using only their thoughts.
-
Space Laser Tech Maps Mysterious Nearshore Terrain
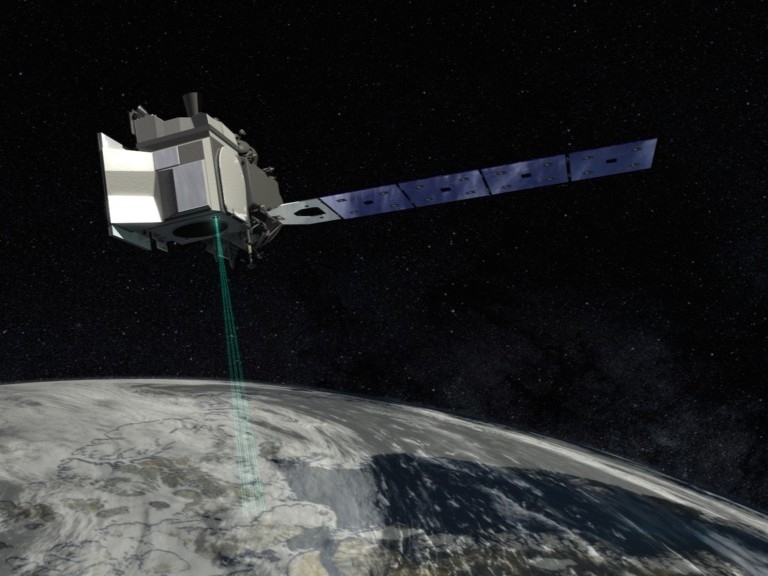

Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin and Oregon State University developed a new technology that uses satellites in space to map the tricky waters just off coastal shores.
-
Stressed or Bored at Work? New Electronic Tattoo Can Help
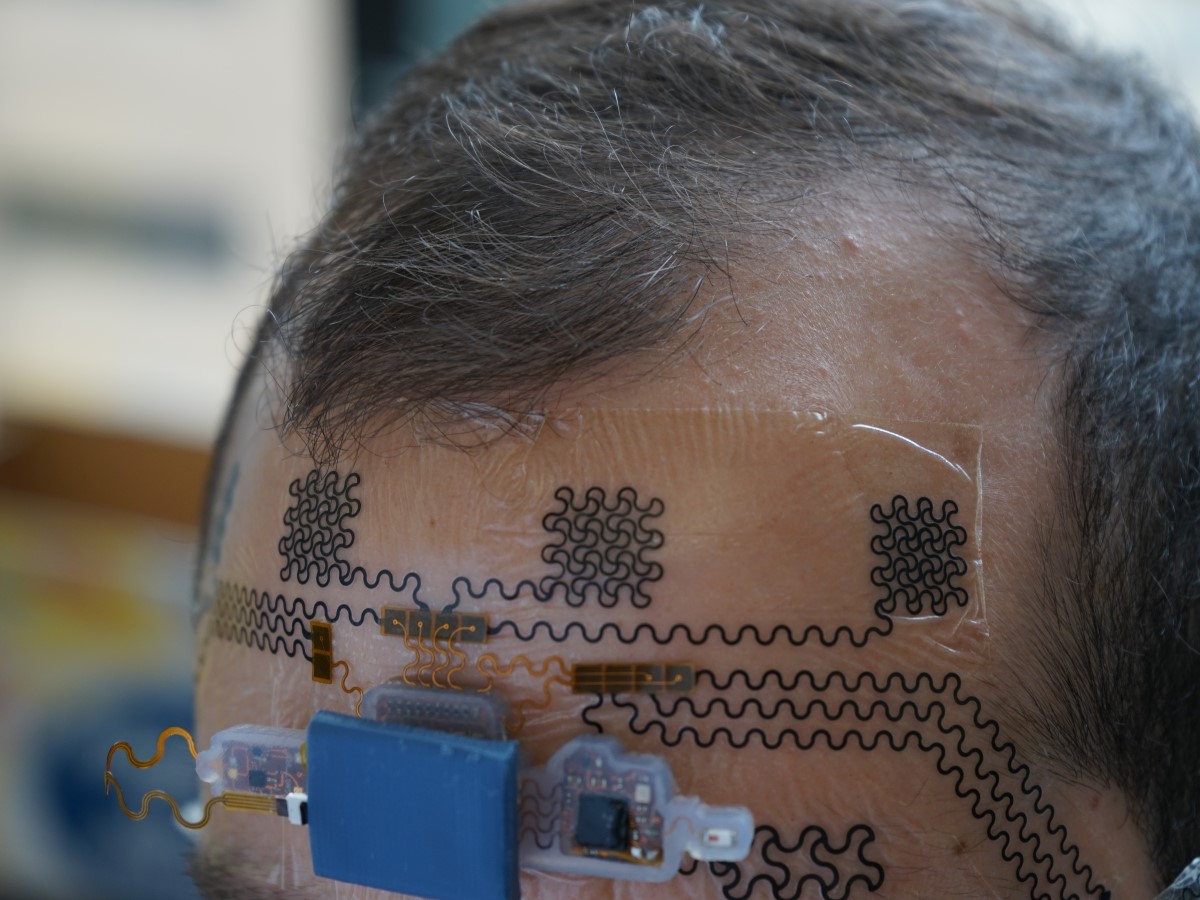
A new wireless forehead e-tattoo created by Texas Engineers decodes brainwaves to measure mental strain without bulky headgear.
-
Unlock Your Computer with a Password-encoded Molecule
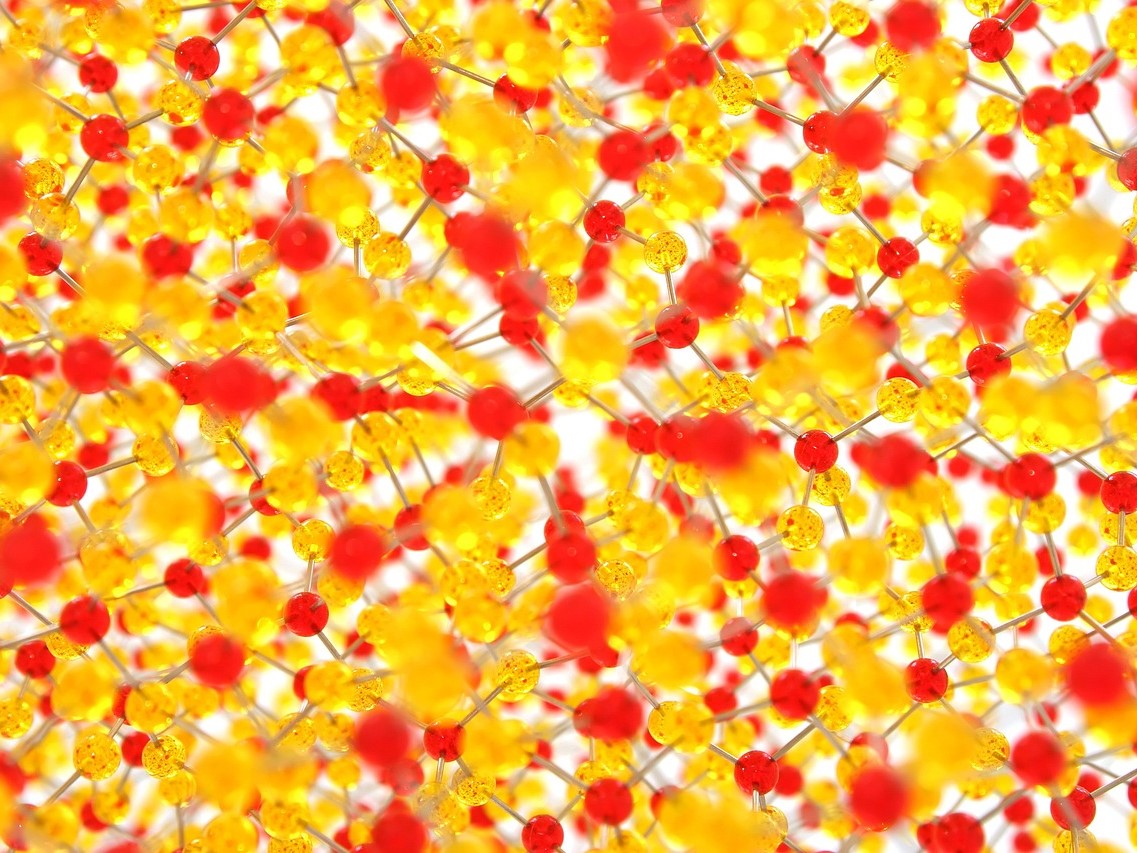
Researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have developed an alternative method to encode information in synthetic molecules, which they used to encode and then decode an 11-character password to unlock a computer.
-
3D Imaging is Moving on Up with Newly Developed Method

Texas Engineers developed an innovative new technique that allows accurate space and time reconstruction of optically scattering samples, even when they're moving.
-
Rare Earth Element Extraction Bolstered by New Research
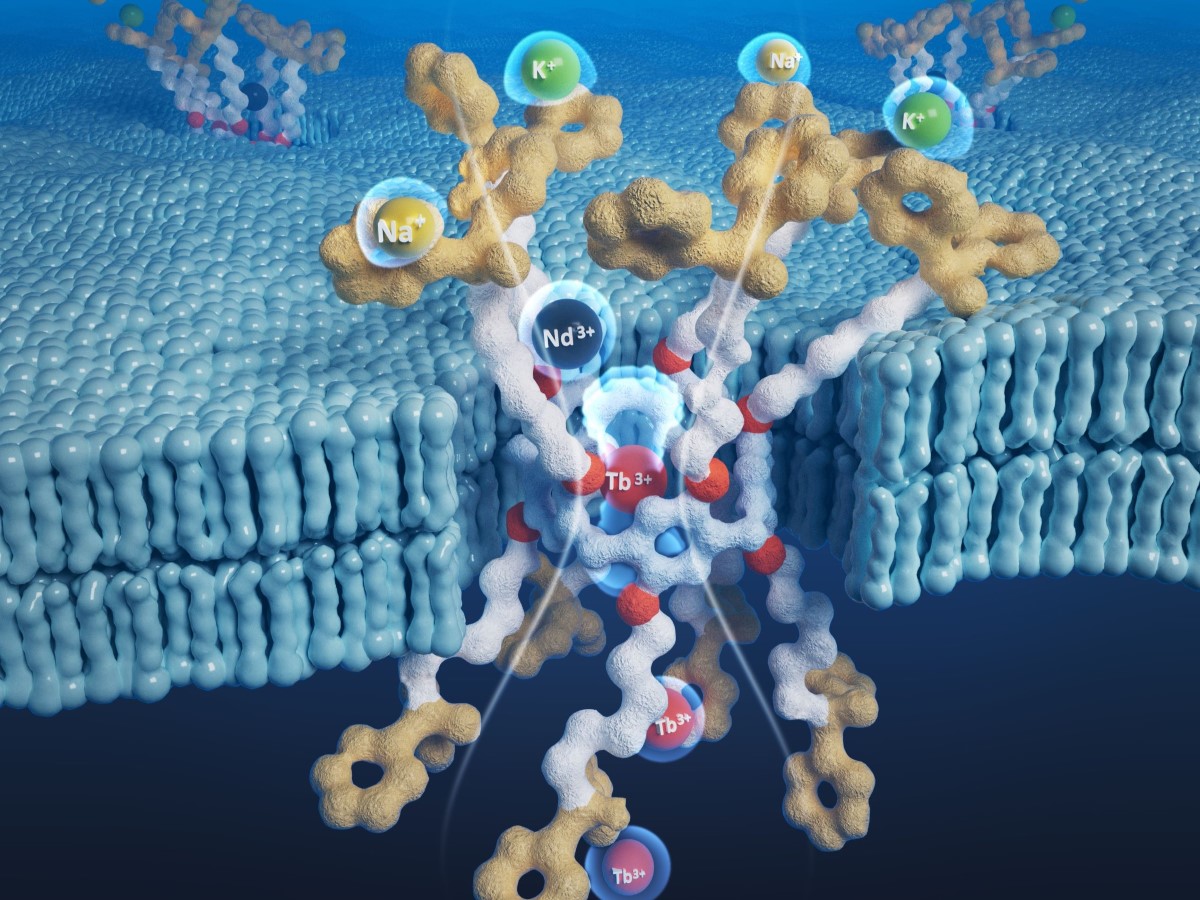
A more efficient and environmentally friendly approach to extracting rare earth elements that power everything from electric vehicle batteries to smartphones could increase domestic supply and decrease reliance on costly imports.
-
Tricking Light with Metaplasmonic Films

Texas Engineers have demonstrated a technique to trick light into behaving as if it was interacting with atomically thin metal films, setting the stage for the design and development of next-generation optoelectronic devices.
-
Smoothing Over Rough Edges in Batteries

Texas Engineers have discovered a new phenomenon in modern batteries, one that could be used to improve their life cycles.
-
No Bones About It: New Details About Skeletal Cell Aging Revealed
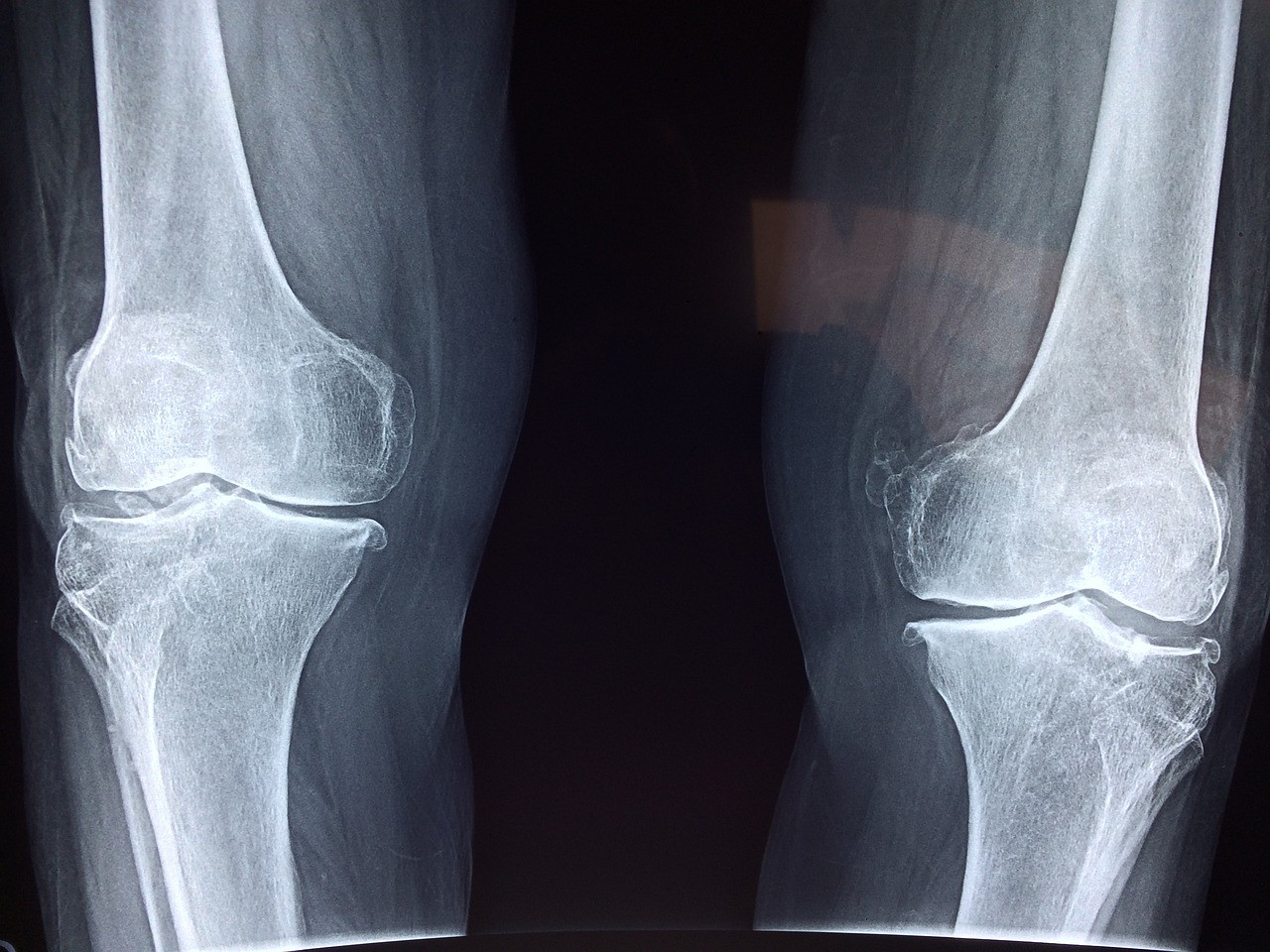
Scientists and researchers around the globe are investigating a series of mysteries about what happens to our bones over time. In a new study, a team led by The University of Texas at Austin, in collaboration with Mayo Clinic and Cedars-Sinai Medical Center just made a major break in the case.
-
New Research Boosts Future Whooping Cough Vaccines
New research from The University of Texas at Austin could aid in improving whooping cough vaccines to once again push this disease toward eradication by targeting two key weaknesses in the infection.
-
A Path to Safer, High-Energy Electric Vehicle Batteries

A new study dives deep into nickel-based cathodes, one of the two electrodes that facilitate energy storage in batteries, to improve electric vehicles.
-
Super Sapphire Resists Scratches, Glare, Fog and Dust
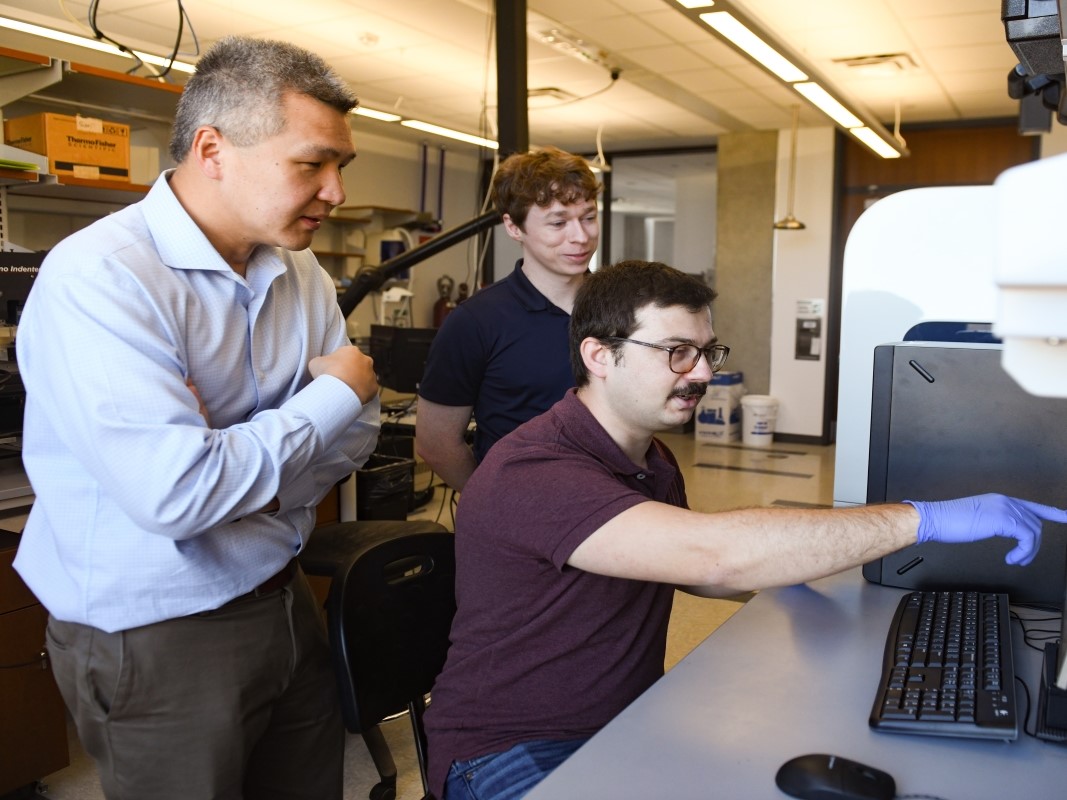

Researchers at The University of Texas at Austin have discovered techniques to bestow superpowers upon sapphire, a material that most of us think of as just a pretty jewel.
-
From Scraps to Sips: Everyday Biomass Produces Drinking Water from Thin Air
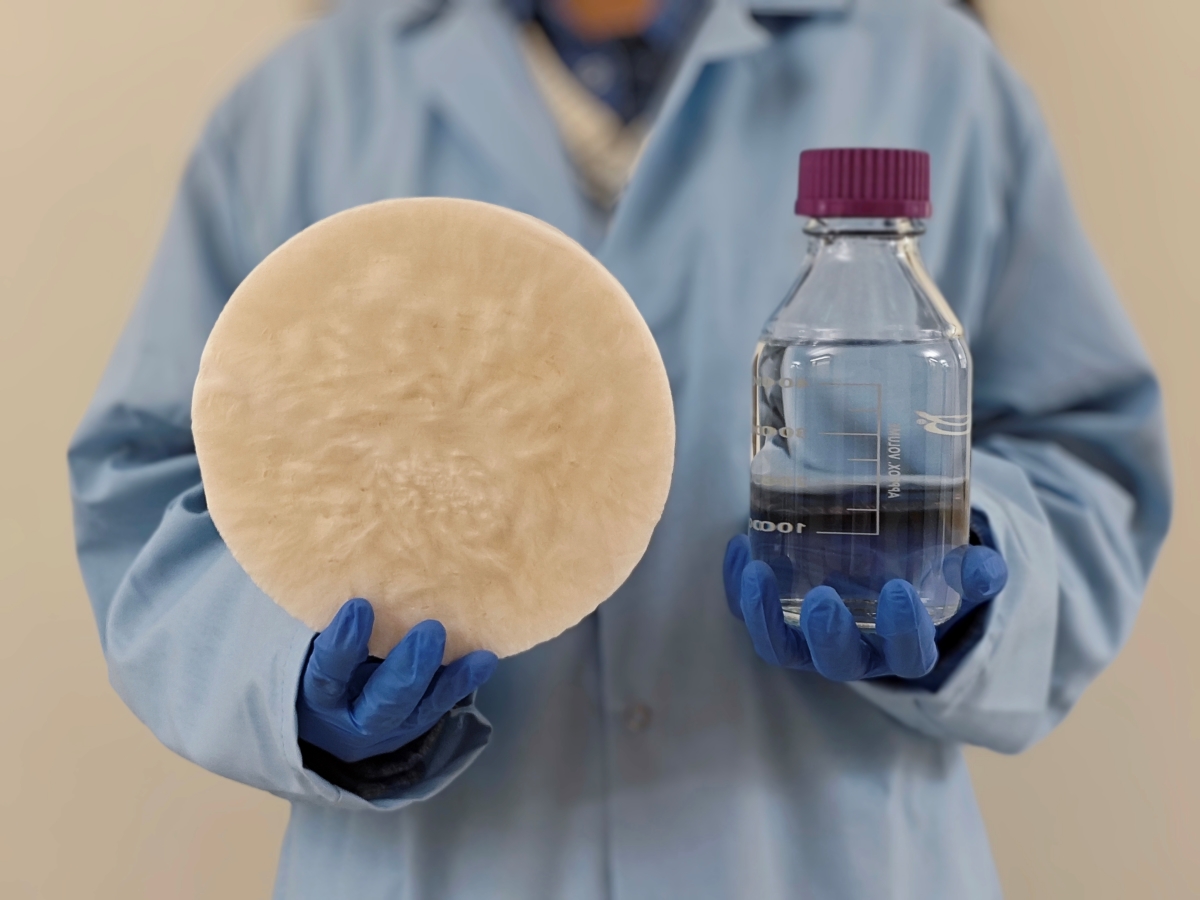

Discarded food scraps, stray branches, seashells and many other natural materials are key ingredients in a new system that can pull drinkable water out of thin air developed by researchers from The University of Texas at Austin.
-
Magnets Emulate Neurons for Next-Generation Computing
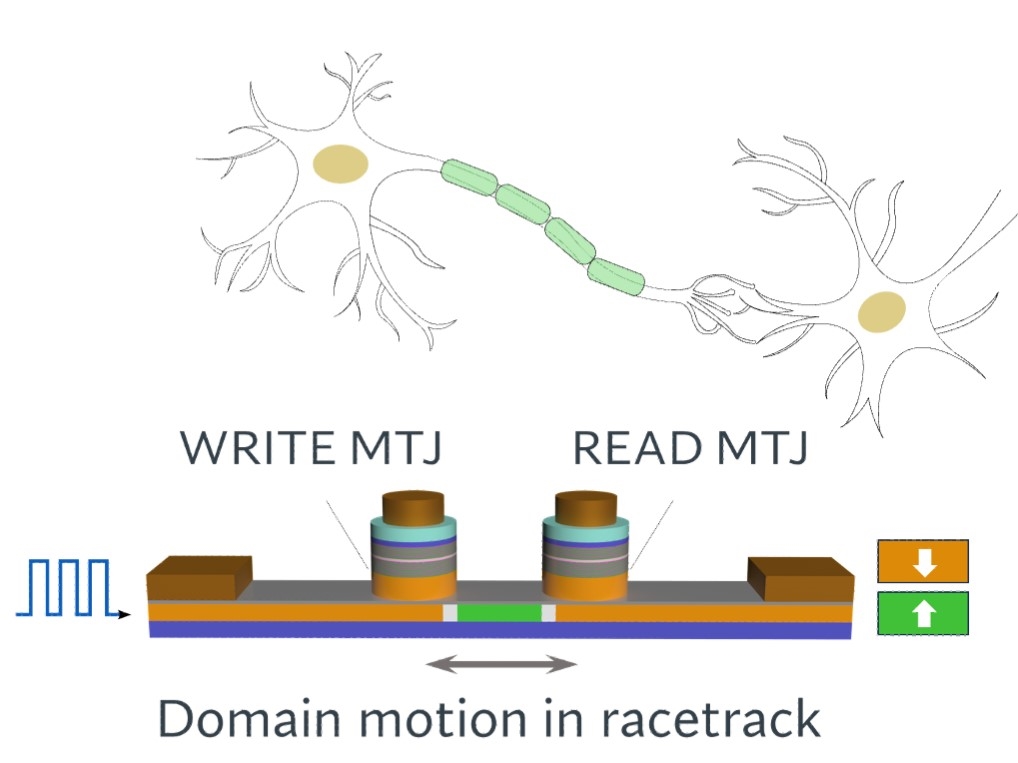
In the quest to bring the next evolution of computing to the masses — electronics that can think like the human brain — researchers from The University of Texas at Austin have achieved several key milestones.
-
Engineering a Better Athlete
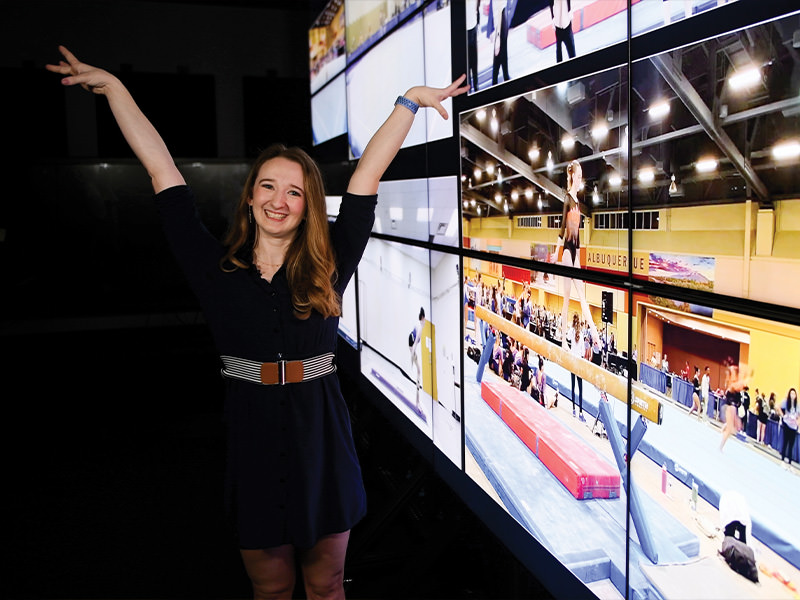

Ella Small knows how to make a big impression, at the doctor’s office and on the balance beam.
-
Chips Ahoy
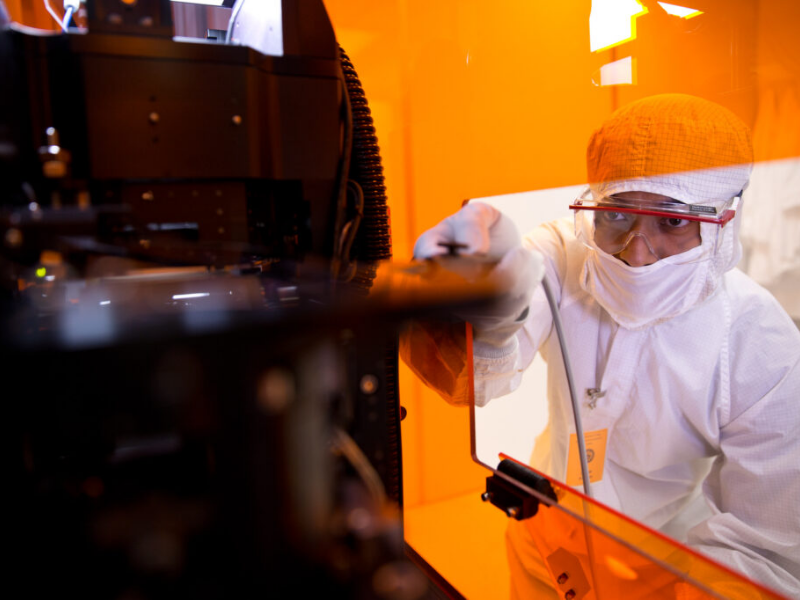

Texas is the capital of the U.S. semiconductor revolution and UT the engine behind it.
-
WTF is Quantum?
Quantum mechanics won’t help you shrink like Ant-Man, but physics really does get weird at the quantum level. For centuries, a set of physical rules governed the behavior of atoms, the building blocks for all matter in the universe...







